Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Giving reason, state whether the following statement is true or false.
When equilibrium price of a good is less than its market price, there will be competition among the sellers.
Solution
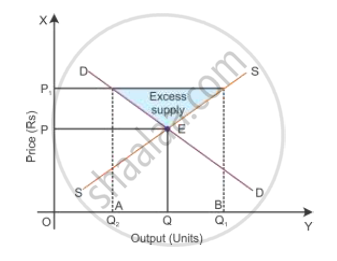
True, when equilibrium price of a good is less than its market price, there will be competition among the sellers. In the diagram, the equilibrium price and quantity are OP and OQ. As the equilibrium price is low for farmers, the government fixes the price floor, i.e. the price level increased from OP to OP1 which leads to a decline in the quantity demand, and therefore, there is excess supply in the market. Here, the competition will increase among the sellers, and hence, the price will come down to the equilibrium point where market demand is equal to market supply.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Determination of equilibrium price under perfect competition.
Explain the chain effects, if the prevailing market price is below the equilibrium price.
If the prevailing market price is above the equilibrium price, explain its chain of effects.
Explain the chain of effects of excess supply of a good on its equilibrium price
X and Y are complementary goods. The price of Y falls. Explain the chain of effects of this change in the market of X.
Explain the chain of an effect of excess demand of a good on it equilibrium price.
Explain the meaning of excess demand and excess supply with the help of a schedule. Explain their effect on equilibrium price.
Distinguish between Gross domestic product at a market price and Gross domestic product at factor cost.
Write explanatory answer.
Define perfect competition and explain price determination under perfect competition.
Define or Explain the General equilibrium.
Define or explain the following concepts (Any THREE):
Effective demand
Suppose the price at which the equilibrium is attained in exercise 5 is above the minimum average cost of the firms constituting the market. Now if we allow for free entry and exit of firms, how will the market price adjust to it?
At what level of price do the firms in a perfectly competitive market supply when free entry and exit is allowed in the market? How is the equilibrium quantity determined in such a market?
Define or explain the following concept:
Equilibrium price
Fill in the blank with appropriate alternative given below
The price at which demand and supply equate to each other is called _______ price.
The diagram given below shows the change in price of cotton shirts. Which one of the following causes the equilibrium price to move from P1 to P2?