Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Which mode of reproduction gives rise to variation?
Solution
Sexual reproduction gives rise to variation.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Give the importance of variation in survival of species.
Name two main processes of sexual reproduction
Oviparous animals give birth to young ones.
A zygote is formed as a result of fertilisation.
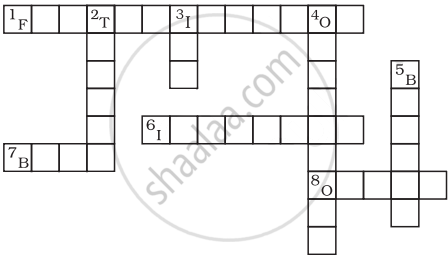
Complete the crossword puzzle using the hints given below.
Across
1. The process of the fusion of the gametes.
6. The type of fertilisation in hen.
7. The term used for bulges observed on the sides of the body of Hydra.
8. Eggs are produced here
Down
2. Sperms are produced in these male reproductive organs.
3. Another term for the fertilised egg.
4. These animals lay eggs.
5. A type of fission in amoeba.
Differentiate between Parthenocarpy and Parthenogenesis. Give one example of each.
Name two animals which reproduce sexually.
In which sort of reproduction are gametes involved?
What is formed when two gametes fuse?
State the advantages of sexual reproduction over asexual reproduction.
Name two plants which reproduce by sexual reproduction method and two plants which reproduce by asexual reproduction methods.
What would be the ratio of chromosome number between an egg and its zygote?
The correct sequence of organs in the male reproductive system for the transport of sperms is:
(a) testis → vas deferens → urethra
(b) testis → ureter → urethra
(c) testis → urethra → ureter
(d) testis → vas deferens → ureter
Put a tick mark (✓) against the correct alternative in the following statement:
Amoeba is most commonly reproduced by:
Put a tick mark (✓) against the correct alternative in the following statement:
Which one of the following represents the correct sequence in the life history of a butterfly ?
- Egg → Larva → Adult → Pupa
- Egg → Pupa → Adult → Larva
- Egg → Larva → Pupa → Adult
- Egg → Pupa → Larva → Adult
Distinguish between the following pair of terms:
Sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction.
Multiple choice question. Tick (✓) the correct choice:
Butterfly in its development from larva to an adult shows
- multiplication
- metamorphosis
- fertilisation
- none of the above
Multiple choice question. Tick (✓) the correct choice:
Which of the following glands is responsible for bringing about changes during adolescence in boys and girls?
- pituitary
- adrenal
- thyroid
- testis
Define the term Adolescence.
How is the chromosome number maintained in sexually reproducing organisms?
Answer the following question.
Explain the histological structure of ovary in human.
Animals which give birth to young ones directly are named as ______.
Choose the correct statement from the following
Name the phenomenon where the female gamete directly develops into a new organism with an avian example.
Identify the correct sequence of events.
In sexual reproduction, offsprings resemble the parents ______.
Oestrus cycle is seen in ______.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Which of the following statements, support the view that elaborate sexual reproductive process appeared much later in the organic evolution.
- Lower groups of organisms have simpler body design
- Asexual reproduction is common in lower groups
- Asexual reproduction is common in higher groups of organisms
- The high incidence of sexual reproduction in angiosperms and vertebrates
______ is the first stage of sexual reproduction.
Name the two ways by which fertilisation in animals takes place.
Explain the two types of fertilization.
Reproduction is essentially a phenomenon that is not for survival of an individual but for the stability of a species. Justify.
Sexual reproduction is characterized by ______
Zygote develop a thick wall that is resistant to dessication and damage is present in ______.
Enumerate the differences between asexual and sexual reproduction. Describe the types of asexual reproduction exhibited by unicellular organisms.
Differentiate between oestrus and menstrual cycles. Cite an example for each type.
Which is a better mode of reproduction, sexual or asexual? Why?
Explain how stability of the DNA of the species is ensured in sexually reproducing organisms.
