Advertisements
Advertisements
Question

“While shopping for fruits in the local market you see many seller selling fruits”. In this context answer the following:
- What is the type of market referred to?
- State and draw the type of demand curve faced by the market above.
- Differentiate between the market indicated above and monopoly on the basis of:
- No. of sellers
- Market price
- Entry and exit of firms in the market
Solution
a. This type of market is referred to as the perfectly competitive market.
b. Perfectly elastic demand curve: It is a situation in which a small change in price causes an infinitely large change in quantity demanded. A small rise in price on the part of the seller reduces the demand to zero. A small reduction in price, will increase the demand to infinity (i.e., no seller is able to satisfy this demand at the reduced price). In our real life, we do not have any such commodity which has perfectly elastic demand. Here, elasticity of demand is equal to infinity and demand curve becomes parallel to X-axis as shown in diagram. Alternatively speaking, here quantity demanded is independent of price. Price is given.
Demand for a good can be perfectly elastic only when there are some perfect substitutes of the good are available in the market. But perfect substitutes are not found in real life.
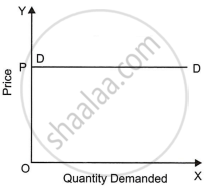
c.
| Basis | Perfect Competition | Monopoly |
| 1. No. of Sellers: | A large number of small sellers. | There exists only a single seller. |
| 2. Market price: | Uniform price prevails in the entire market and every firm here is a price-taker. | A monopoly firm may or may not charge uniform prices from their different buyers. The firm here is a price-maker. |
| 3. Entry and Exit: | A firm can freely enter into or exit from the market. | The monopoly firm has substantial control over the market price. Thus, each firm is a price maker here. |
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
How is Perfect competitive market is different from a monopoly market?
'A few big sellers' is a characteristic of ______.
In monopolistic competition, there are ______.
Match the following and select the correct option:
| Column I | Column II | ||
| (i) | Perfect competition | (A) | Differentiated Products |
| (ii) | Monopoly | (B) | Few large firms |
| (iii) | Monopolistic Competition | (C) | Single seller |
| (iv) | Oligopoly | (D) | Homogeneous products |
There is no difference between perfect competition and pure competition.
Identify the market form for the following:
Railways in India.
Explain any four features of perfect competition.
Which type of market structure is the following? Give reason.
Mobile phone services
Why can a monopolist charge different prices in different markets?
Mention one feature of a monopoly market.
