Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
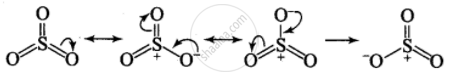
Why does SO3 act as an electrophile?
Solution
Three highly electronegative oxygen atoms are attached to sulphur atom. This makes sulphur atom electron deficient. Due to resonance, sulphur also acquires positive charge. Both these factors make SO3 an electrophile.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What are electrophiles and nucleophiles? Explain with examples.
Identify the reagents shown in bold in the following equation as nucleophiles or electrophiles:
\[\ce{C6H6 + \underline{\text{CH}_3\overset{+}{\ce{C}}{\ce{O}}} -> C6H5COCH3}\]
The reaction: \[\ce{CH_3CH_2I + KOH_{(aq)} -> CH_3CH_2OH + KI}\] is classified as ______.
Identify the reagents shown in bold in the following equation as nucleophiles or electrophiles:
\[\ce{CH3COOH + \underline{\ce{H}\overset{-}{\ce{O}}} -> CH3COO^- + H2O }\]
Identify the reagents shown in bold in the following equation as nucleophiles or electrophiles:
\[\ce{CH3COCH3 + \underline{\overset{-}{\ce{C}}\ce{N}} -> (CH3)2C(CN)(OH)}\]
Electrophiles are electron seeking species. Which of the following groups contain only electrophiles?
(i) \[\ce{BF3, NH3, H2O}\]
(ii) \[\ce{AlCl3, SO3, NO^{+}2}\]
(iii) \[\ce{NO^{+}2, CH^{+}3, CH3 - \overset{+}{C} = O}\]
(iv) \[\ce{C2H^{-}5, \overset{\bullet}{C2}H5, C2H^{+}5}\]
Nucleophile is a species that should have:
(i) A pair of electrons to donate
(ii) Positive charge
(iii) Negative charge
(iv) Electron-deficient species
Match the terms mentioned in Column I with the terms in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Carbocation | (a) Cyclohexane and 1-hexene |
| (ii) Nucleophile of | (b) Conjugation of electrons of C – H σ bond with empty p-orbital present at adjacent positively charged carbon. |
| (iii) Hyperconjugation | (c) sp2 hybridised carbon with empty p-orbital |
| (iv) Isomers | (d) Ethyne |
| (v) sp hybridisation | (e) Species that can receive a pair of electrons |
| (vi) Electrophile | (f) Species that can supply a pair of electrons |
