Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Why does velocity increase when water flowing in broader pipe enters a narrow pipe?
Solution
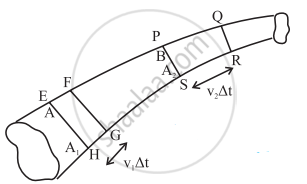
Consider a tube of flow as shown in the figure. All the fluid that passes through a tube of flow must pass through any cross section that cuts the tube of flow. Consider section A1 and A2 located at points A and B respectively. If mass m of the fluid enters the section A1 then equal mass of fluid should leave the section A2.
By the equation of continuity,
A1v1 = A2v2
∴ v2 = (A1/A2)v1
For the same volume to pass points A and B in a given time, the speed must be greater at point B.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Multiple Choice Question.
Two hailstones with radii in the ratio of 1:4 fall from a great height through the atmosphere. Then the ratio of their terminal velocities is
With what terminal velocity will an air bubble 0.4 mm in diameter rise in a liquid of viscosity 0.1 Ns/m2 and specific gravity 0.9? Density of air is 1.29 kg/m3.
Calculate the viscous force acting on a raindrop of diameter 1 mm, falling with a uniform velocity of 2 m/s through air. The coefficient of viscosity of air is 1.8 × 10-5 Ns/m2.
A horizontal force of 1 N is required to move a metal plate of area 10-2 m2 with a velocity of 2 × 10-2 m/s, when it rests on a layer of oil 1.5 × 10-3 m thick. Find the coefficient of viscosity of oil.
Two stones with radii 1:2 fall from a great height through the atmosphere. Their terminal velocities are in the ratio ______
What is the net weight of a body when it falls with terminal velocity through a viscous medium?
A square metal plate of area 100 cm2 moves parallel to another plate with a velocity of 10 cm/s, both plates immersed in water. If the viscous force is 200 dyne and the viscosity of water is 0.01 poise, what is the distance between them?
The relative velocity between two parallel layers of water is 8 cm/s and the perpendicular distance between them is 0.1 cm. Calculate the velocity gradient.
A raindrop of radius 0.3 mm falls through the air with a terminal velocity of 1 m/s. The viscosity of air is 18 x 10−6 Ns /m2. Find the viscous force on the raindrop.
The speed at which the flow of water in a long cylindrical pipe of diameter 6 cm becomes turbulent is ______
(The viscosity of water = 1 x 10-3 Pa.s and for the onset of turbulent flow in a long cylindrical pipe, Reynolds number = 3000)
Reynold's number is less for ______.
Water is flowing through a tube of diameter 1 cm at 6 cm/s. Taking `eta` = 10-2 poise the flow of liquid and Reynold's number are ____________.
The maximum average velocity of water in a tube of diameter 4 cm so that the flow becomes laminar is [Viscosity of water is 10-3 N m-1, take Rn = 200] ____________.
The Reynold's number for a liquid flow in a tube does NOT depend on ______.
State the formula for critical velocity in terms of Reynold's number for a flow of a fluid.
If p is the density and η is coefficient of viscosity of fluid which flows with a speed v in the pipe of diameter d, the correct formula for Reynolds number Re is ______.
What are the two main causes of turbulent flow?
