Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Why is the equality between marginal cost and marginal revenue necessary for a firm to be in equilibrium? Is it sufficient to ensure equilibrium? Explain.
Solution
The producer’s equilibrium refers to the situation in which he maximises his profits. A
producer strikes an equilibrium when two conditions are satisfied.
i. MR = MC
ii. MC is rising or the MC curve cuts the MR curve from below.
MR, MC Schedule and Producer’s Equilibrium:
| Output | MR | MC |
| 1 | 10 | 8 |
| 2 | 10 | 7 |
| 3 | 10 | 6 |
| 4 | 10 | 8 |
| 5 | 10 | 10 |
| 6 | 10 | 13 |
Here, it is assumed that price (AR) is constant so that MR is constant, i.e. = Rs 10 under perfect competition. This table indicates that the two conditions of equilibrium are satisfied only when 5 units of output are produced. It is here that (i) MR = MC = Rs 10 and (ii) MC is rising.
Equilibrium is not struck when MR > MC. In such a situation, producing an additional unit would add more to TR than to TC. This implies that the gap between TR and TC tends to widen or that profits are still to be maximised.
Condition 1:
i. If MR > MC:
Suppose OQ1 is the output level at the price AQ1 and the marginal cost is BQ1, then it would be AQ1 > BQ1. Here, OQ1 is not the level of output at which the profit is maximised. So, the firm can increase its profit by increasing the production to the OQ2 level of output.
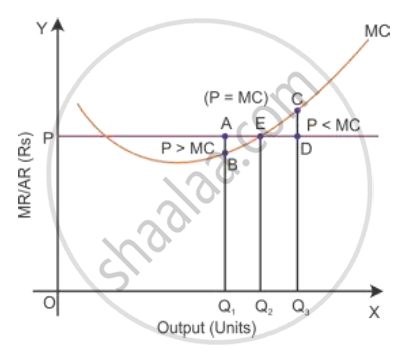
ii. If Price (MR) < MC
Suppose OQ3 is the output level at the price DQ3 and the marginal cost is CQ3, then it would be DQ3 < CQ3. Here, OQ3 is not the level of output at which the profit is maximised. So, the firm can increase its profit by decreasing its output level to OQ2. Thus, the firm’s equilibrium level of output to maximise output is that MR = MC and MC should be rising at the point of intersection with MR.
Condition 2:
In the given diagram, the MC curve intersects the price line (or MR) at two points—A and B.
Here Condition 1 of profit maximisation MR = MC is satisfied at these two points. Next, let
us consider Condition 2.
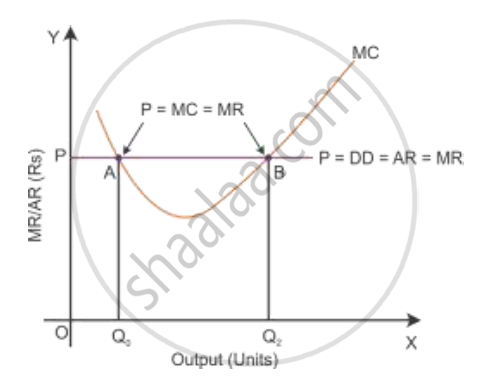
i. Intersection point at A
At intersection point A, the price is equal to MC but MC is falling, and it is a downward-sloping curve. If the output is increased more than the OQ0 level, then the price is more than MC. This means that the firm can increase the production more than the OQ0 level of output to maximise profit.
ii. Intersection point at B
At intersection point B, if the output is increased more than output OQ2, the price is more than MC. This states that the firm can increase the production more than the OQ2 level of output to maximise profit. While if the firm produces a higher level of output than OQ2, then the price is less than MC. This clearly states that high profit is possible by decreasing the output level to OQ2. Thus, Point B is the producer’s equilibrium and OQ2 is the output level to maximise profit by satisfying the two necessary conditions (i) Price = MC and (ii) the MC curve is rising.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
From the following information about a firm, find the firms equilibrium output in terms of marginal cost and marginal revenue. Give reasons. Also find profit at this output
| Output (units) | Total Revenue (Rs) | Total Cost (Rs) |
| 1 | 7 | 8 |
| 2 | 14 | 15 |
| 3 | 21 | 21 |
| 4 | 28 | 28 |
| 5 | 35 | 36 |
Explain the conditions of producer’s equilibrium with the help of a numerical example.
Explain the conditions of a producer's equilibrium in terms of marginal cost and marginal revenue. Use diagram.
Given below is the cost schedule of a product produced by a firm. The market price per unit of the product at all levels of output is Rs12. Using marginal cost and marginal revenue approach, find out the level of equilibrium output. Give reasons for your answer
| Output (units) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| Average Cost (Rs.) | 12 | 11 | 10 | 10 | 10.4 | 11 |
Using marginal cost and marginal revenue approach, find out the level of output at which producer will be in equilibrium. Give reasons for your answer
| Output (units) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| Average Revenue (Rs) | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Total Cost (Rs) | 22 | 42 | 60 | 76 | 96 | 120 |
Explain why will a producer not be in equilibrium if the conditions of equilibrium are not met.
Explain the conditions of producer's equilibrium under perfect competition.
From the following table, find out the level of output at which the producer will be in equilibrium. Give reasons for your answer.
|
Output (units) |
Marginal Revenue Rs |
Marginal Cost Rs |
|
1 |
8 |
10 |
|
2 |
8 |
8 |
|
3 |
8 |
7 |
|
4 |
8 |
8 |
|
5 |
8 |
9 |
With the help of the given schedule, determine the firm's equilibrium using marginal revenue − marginal cost approach. Give valid reasons in support of your answer.
| Output (in units) |
Total revenue (TR) (in ₹) | Total Cost (TC) ( in ₹) |
| 1 | 20 | 20 |
| 2 | 40 | 30 |
| 3 | 60 | 36 |
| 4 | 80 | 40 |
| 5 | 100 | 60 |
| 6 | 120 | 90 |
Answer the following question.
Explain the conditions of the producer's equilibrium with the help of a numerical example. Use marginal cost and marginal revenue approach.
Fill in the blank.
"For a firm to be in equilibrium, Marginal Revenue (MR) and Marginal Cost (MC) must be __________ and beyond that level of output Marginal Cost must be ____________."
What is meant by accounting cost?
