Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Why is the base of a transistor made thin and is lightly doped?
Solution
The base of a transistor is lightly doped than the emitter and narrowed so that almost all electrons injected from the emitter (in a n-p-n transistor) diffuse right across the base to the collector junction without recombining with holes. In other words, the base width is kept smaller than the recombination distance. In addition, to improve emitter efficiency and common-base current gain α, the emitter is much more heavily doped than the base.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Why are the emitter, the base, and the collector of a BJT doped differently?
In a common-base connection, a certain transistor has an emitter current of 10mA and a collector current of 9.8 mA. Calculate the value of the base current.
In a transistor amplifier, IC = 5.5 mA , IE = 5.6 mA. The current amplification factor β is ______
Draw the circuit symbol of the PNP transistor.
The light emitted in an LED is due to
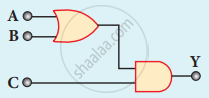
The output of the following circuit is 1 when the input ABC is
Give the Barkhausen conditions for sustained oscillations.
Explain the current flow in an NPN transistor.
Sketch the static characteristics of a common emitter transistor and bring out the essential features of input and output characteristics.
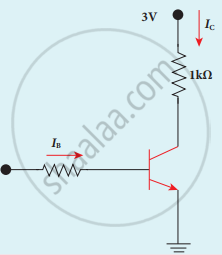
Assuming VCEsat = 0.2 V and β = 50, find the minimum base current (IB) required to drive the transistor given in the figure to saturation.
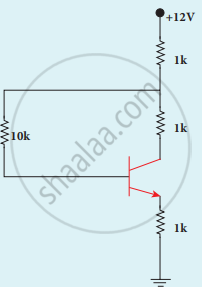
A transistor of α = 0.99 and VBE = 0.7 V is connected in the common-emitter configuration as shown in the figure. If the transistor is in the saturation region, find the value of collector current.
The condition to convert an amplified signal into an oscillating signal is ______
Ve, Vb, and Ve are emitter, base, and collector voltage respectively for npn transistor in CE mode. Amplifier works for the combination of biasing voltage equal to ______.
If `alpha`-current gain of a transistor is 0.98. What is the value of `beta`- current gain of the transistor?
In an npn transistor, the base current is 100 µA and the collector current is 10 mA. The emitter current is ______.
ln switching circuit, transistor is in ON state and values of IC and IB are 4.2 mA and 5 µA respectively and RC= l k`Omega` and RB= 300 k`Omega`. If VBE = 0.5 V, find the value of VBB.
Which of the following regions of a transistors are, respectively, heavily dopped and lightly dopped?
For a common emitter configuration, if 'α' and 'β' have their usual meanings, the correct relationship between 'α' and 'β' is ______.
In a silicon transistor, a change of 7.89 mA in the emitter current if produces a change of 7.8 mA in the collector current, then the base current must change by ____________.
A pnp transistor is used in common-emitter mode. If a change of 40 µA in base current brings a change of 2 µA in collector current with 0.04 V in base-emitter voltage, then the input resistance is ____________.
The current gain `alpha` of a transistor is 0.95. The change in collector current corresponding to a change of 0.4 mA in the base current in a common emitter arrangement is ______.
In transistor amplifier, base-emitter junction is forward biased and collector emitter junction is reverse biased. The current gain is ______.
In common emitter amplifier, a change of 0.2 mA in the base current causes a change of 5 mA in the collector current. If input resistance is 2K `Omega` and voltage gain is 75, the load resistance used in the circuit is ______.
The reverse bias in a junction diode is changed from 8V to 13V, then the value of the current changes from 40μA to 60μA. The resistance of junction diode will be ______.
The base current in common emitter mode of the transistor changes by 10 µA. If the current gain of the transistor is 50, then change in collector current is ______.
The current amplification factor for a transistor in its common emitter mode is 50. The current amplification factor in the common base mode of the transistor is ______.
Define α.
