Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
With the help of ciliary muscles the human eye can change its curvature and thus alter the focal length of its lens. State the changes that occur in the curvature and focal length of the eye lens while viewing (a) a distance object, (b) nearby objects.
Solution
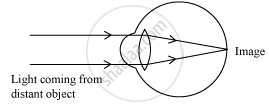
(a) When we see distant object, the ciliary muscles relax/expand to decrease the curvature and there by increase the focal length of the lens. Hence, the lens becomes thin. This enables us to see the distant object clearly. Thus, the focal length of the eye lens increases while seeing distant objects.
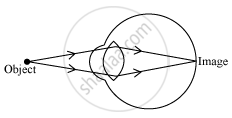
(b) To see the nearby objects clearly, the focal length of the lens should be shorter. For this, the ciliary muscles contract to increase the curvature and thereby decrease the focal length of the lens. Hence, the lens becomes thick. This enables you to see the nearby objects clearly.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Give the scientific names of the following parts of the eye:
changes shape to focus a picture on the retina.
The descriptions of five kinds of images are given below:
(a) diminished and virtual
(b) enlarged and real
(c) enlarged and erect
(d) real and inverted
(e) virtual and the same size
Which one of these describes the image formed:
(i) on the retina of the eye?
(ii) by a magnifying glass?
(iii) by a convex driving mirror on a car?
(iv) by a plane mirror?
(v) on the screen of a slide projector?
Having two eyes gives a person:
(a) deeper field of view
(b) coloured field of view
(c) rear field of view
(d) wider field of view
With reference to the functioning of the eye, answer the question that follow:
What is the shape of the lens during near vision?
State the Function:
Conjunctiva
Choose the Odd One Out:
Write the function of the human eye and label parts of the figure given below.

Complete the paragraph by choosing the right options given below.
(minimum, near point, 25 cm, farthest, farthest distance, far point)
The _______ distance of an object from a normal eye, at which it is clearly visible without stress on the eye, is called the minimum distance of distinct vision. The position of the object at this distance is called the _______ of the eye, for a normal human eye, the near point is at _______. The _______ distance of an object from a human eye, at which it is clearly visible without stress on the eye is called _______ of distinct vision. The position of the object at this distance is called the _______ of the eye.
______ is tough and thick white sheath that protects the inner parts of the eye.
What kind of lens is there in our eyes? Where does it form the image of an object?
