Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Write the factors influencing the basicity of amines.
Solution
Factors influencing the basicity of amines are as follows:
- Influence of +I effect:
1. Basicity of amines is related to the structural effects which influence the stabilization of various species. Greater is the stabilization of the protonated amine, that is, the conjugate acid, greater is the basicity of the amine.
2. An alkyl group exerts an electron releasing inductive effect (+I) which stabilizes the positive charge on the atom bonded to it. As we move from conjugate acid of ammonia \[\ce{NH^+_4}\] to that of tertiary amine (R3NH+), the number of alkyl groups (R) bonded to nitrogen goes on increasing steadily. This results in increasing stabilization of the conjugate acids and thereby an increasing order of basic strength is expected.
Order of stabilization: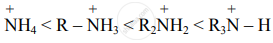
Expected order of basic strength: NH3 < R – NH2 < R2NH < R3N
3. The expected order of basic strength on the basis of the +I effect differs from the observed order. However, decreased basic strength of 3° amine implies that the conjugate acid of 3° amine is less stabilized even though the +I effect of three alkyl groups in R3N+H is expected to be large. Decreased basic strength of 3° amine implies that the conjugate acid of 3° amine is less stabilized even though the +I effect of three alkyl groups in R3N+H is expected to be large. This is suggestive of the existence of another influencing factor in the stabilization of conjugate acids of amines. - Influence of solvation by water: The solvent water stabilizes the conjugate acid by hydrogen bonding through the ‘H’ bonded to the ‘N+’.
The number of ‘H’ atoms bonded to the ‘N+’ decreases from 4 in \[\ce{NH^+_4}\] to 1 in R3NH+. As a result, \[\ce{NH^+_4}\] is best stabilized by solvation while the stabilization by solvation is very poor in R3NH+. Thus, the basic strength of 3° amines is decreased. - Combined influence of +I effect and solvation:
1. The combined influence of both, +I effect and solvation on stabilization if conjugate acids of aliphatic amines decide the observed basic strength and pKb value. These two influencing factors operate in opposite directions.
2. The net result is that as we move from NH3 to RNH2 to R2NH, the basic strength increases due to better stabilization of the corresponding conjugate acids.
3. But, 3° amine is a weaker base than 2° amine because the stabilization of conjugate acid of 3° amine by solvation is very poor.
RELATED QUESTIONS
Choose the most correct option.
Which of the following has the highest basic strength?
Answer in one sentence.
Write the order of the basicity of aliphatic alkylamine in the gaseous phase.
Answer in one sentence.
Why are primary aliphatic amines stronger bases than ammonia?
Answer in one sentence.
Arrange the following amines in the increasing order of their pKb values.
Aniline, Cyclohexylamine, 4-Nitroaniline
The strongest base amongst the following is
Distinguish between methanamine, dimethanamine and trimethanamine using Hinsberg’s reagent.
The CORRECT decreasing order of the basic strength of amines in aqueous solution is:
IUPAC name of p-toluidine is ____________.
When X is treated with ethanoyl chloride in presence of pyridine, N-methyl-N-phenylethanamide is formed. Identify compound X.
In the following compounds, the decreasing order of basic strength will be _______________.
Identify the gas liberated when ethylamine is treated with NaNO2/HCl at 273 K.
Which of the following is a weaker base than ammonia?
Which of the following is a simple, aliphatic 3° amine?
In which of the following pairs, the first compound is more basic than the second compound?
Nitrogen atom in amines is ____________.
High basicity of Me2NH relative to Me3N in aqueous solution is attributed to ______.
Which of the following is incorrectly matched?
Why are aliphatic amines are stronger bases than ammonia?
