Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Write the ionization of sulphuric acid showing the formation of hydronium ion.
Solution 1
Ionization of sulphuric acid showing the formation of hydronium ion:
H2SO4 + H2O  H3O+ + HSO4-
H3O+ + HSO4-
HSO4- + H2O  H3O+ + SO42-
H3O+ + SO42-
Solution 2
Water is a polar molecule which is represented as
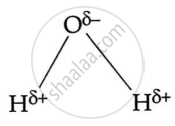
When acid dissolves in water, it interacts strongly with polar molecules, forming a proton [H+]. This proton cannot exist independently in an aqueous solution and attaches to a water molecule to create a hydrogen ion.
\[\ce{HCl <=>[H2O] H+ + Cl^1-}\]
\[\ce{H^1+ + H2O <=> \underset{(Hydronium ion)}{[H3O^1+]}}\]
or \[\begin{bmatrix}\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H - \overset{\bullet\bullet}{\mathbf{O}} - H}\\
\downarrow\\
\ce{H}\\
\end{array}\end{bmatrix}^+\]
and \[\ce{H2SO4 + 2H2O <=> 2[H3O]+ + [SO4]^2-}\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain the following:
Carbonic acid gives an acid salt but hydrochloric acid does not.
Give an equation to show how the following is made from their corresponding anhydride.
carbonic acid
Identify the odd one out and justify.
Explain the following:
Nitrogen dioxide is a double acid anhydride.
How are acids classified based on ionization? Give examples.
Match the following:
| 1. | Hydrochloric acid | a. | Fertilizer |
| 2. | Citric acid | b. | Baking powder |
| 3. | Nitric acid | c. | Car batteries |
| 4. | Oxalic acid | d. | Cleansing agent in toilets |
| 5. | Sulphuric acid | e. | Removing black stains |
| f. | Effervescent salts |
Explain the following:
H3PO3 is not a tribasic acid
Give the basicity of sulphuric acid.
Name the acidic anhydride of the following acid:
Phosphoric acid
Name the acidic anhydride of the following acid:
Carbonic acid
