Advertisements
Advertisements
Write the definition of a function SumEO(int VALUES[], int N) in C++, which should display the 4 sum of even value and sum of odd values of the array separately.
Example: If the array VALUES contains
| 25 | 20 | 22 | 21 | 53 |
Then the functions should display the output as:
Sum of even values = 42 (i.e., 20+22)
Sum of odd values= 99 (i.e., 25+21+53)
Concept: One and Two Dimensional Arrays - Sequential Allocation and Address Calculation
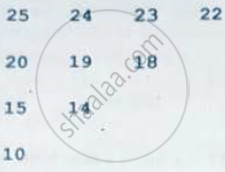
Write a definition for a function UpperHalf(int Mat[4][4]) in C++ which displays the elements in the same way as per the example is shown below.
For example, if the content of the array Mat is as follows:
| 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 |
| 20 | 19 | 18 | 17 |
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 |
| 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 |
Thew function should display the content in the following format:
Concept: One and Two Dimensional Arrays - Sequential Allocation and Address Calculation
Let us assume Data[20][15] is a two-dimensional array, which is stored in the memory along the row with each of its elements occupying 2 bytes. Find the address of the element Data(10][5], if the element Data[10][l5] is stored at the memory location 15000.
Concept: One and Two Dimensional Arrays - Sequential Allocation and Address Calculation
Wnte the definition of a member function AddPac ket() for a class QUEUE in C++, to remove/delete a Packet from a dynamically allocated QUEUE of Packets' considering the following code is already written as a part of the program.
struct Packet
{
int PID;
char Address[20];
Packet *LINK;
};
class QUEUE
{
Packet *Front, *Rear;
public:
QUEUE(){Front=NULL;Rear=NULL;}
void AddPacket();
void DeletePacket();
~QUEUE();
};Concept: Queue (Array and Linked Implementation)
ARR[15] ft:20] is a two-dimensional array, which is stored in the memory along the row with each of its elements occupying 4 .bytes. Find the .address of the element ARR[5)[15], if the element ARR[lO] [5] is stored at the memory location 35000.
Concept: One and Two Dimensional Arrays - Sequential Allocation and Address Calculation
A two-dimensional array ARR[50][20] is stored in the memory along the row with each of its elements occupying 4 bytes. Find the address of the element ARR[30] [10], if the element ARR[10] [5] is stored at the memory location 15000.
Concept: One and Two Dimensional Arrays - Sequential Allocation and Address Calculation
Write a function REVROW(int P[] [5], int N, int M) in C++ to display the content of a two-dimensional array, with each row content in reverse order.
For example, if the content of the array is as follows:
| 15 | 12 | 56 | 45 | 51 |
| 13 | 91 | 92 | 87 | 63 |
| 11 | 23 | 61 | 46 | 81 |
The function should display output as

Concept: One and Two Dimensional Arrays - Sequential Allocation and Address Calculation
Observe the following tables VIDEO and MEMBER carefully and write the name of the RDBMS operation out of (i) SELECTION (ii) PROJECTION (iii) UNION (iv) CARTESIAN PRODUCT, which has been used to produce the output as shown below. Also, find the
Degree and Cardinality of the final result.
TABLE: VlDEO
| VNO | VNAME | TYPE |
| F101 | The Last Battle | Fiction |
| C101 | Angels and Devils | Comedy |
| A102 | Daredevils | Adventure |
TABLE: MEMBER
| MNO | MNAME |
| M101 | Namish Gupta |
| M102 | Sana Sheikh |
| M103 | Lara James |
TABLE: FINAL RESULT
| VNO | VNAME | TYPE | MNO | MNAME |
| F101 | The Last Battle | Fiction | M101 | Namish Gupta |
| F101 | The Last Battle | Fiction | M102 | Sana Sheikh |
| F101 | The Last Battle | Fiction | M103 | Lara James |
| C101 | Angels and Devils | Comedy | M101 | Namish Gupta |
| C101 | Angels and Devils | Comedy | M102 | Sana Sheikh |
| C101 | Angels and Devils | Comedy | M103 | Lara James |
| A102 | Daredevils | Adventure | M101 | Namish Gupta |
| A102 | Daredevils | Adventure | M102 | Sana Sheikh |
| A102 | Daredevils | Adventure | M103 | Lara James |
Concept: Relational Data Model
Write SQL queries for (i) to (iv) and find outputs for SQL queries (v) to (viii) which are based on the table.
TABLE: Account
| ANO | ANAME | ADDRESS |
| 101 | Nirja Singh | Bangalore |
| 102 | Rohan Gupta | Chennai |
| 103 | Ali Reza | Hyderabad |
| 104 | Rishabh Jain | Chennai |
| 105 | Simran Kaur | Chandigarh |
TABLE: TRANSACT
| TRNO | ANO | AMOUNT | TYPE | DOT |
| T001 | 101 | 2500 | Withdraw | 2017-12-21 |
| T002 | 103 | 3000 | Deposit | 2017-06-01 |
| T003 | 102 | 2000 | Withdraw | 2017-0S-12 |
| T004 | 103 | 1000 | Deposit | 2017-10-22 |
| T005 | 101 | 12000 | Deposit | 2017-11-06 |
1) To display details of all transaction of TYPE Depos1t from Table TRANSACT.
2) To display the ANO and AMOUNT of all Depos1ts and Withdrawals done in the month of October 2017 from table TRANSACT.
3) To display the last date of the transaction (DOT) from the table TRANSACT for the Accounts having ANO as 103
4) To display all ANO, ANAME and DOT of those persons from tables ACCOUNT and TRANSACT who have done transactions less than or equal to 3000?
5) SELECT ANO, ANAME FROM ACCOUNT WHERE ADDRESS NOT IN ('CHENNAI', 'BANGALORE');
6) SELECT DISTINCT ANO FROM TRANSACT
7) SELECT ANO, COUNT(*), MIN(AMOUNT) FROM TRANSACT GROUP BY AND HAVING COUNT(*) > 1;
8) SELECT COUNT(*), SUM(AMOUNT) FROM TRANSACT WHERE DOT <= '2017-06-01'
Concept: Structured Query Language Advantages of Using SQL
Observe the following table MEMBER carefully and write the name of the RDBMS operation out of (i) SELECTION (ii) PROJECTION (iii) UNION (iv) CARTESIAN PRODUCT, which has been used to produce the output as shown in RESULT. Also, find the Degree and Cardinality of the RESULT :
MEMBER
| NO | MNAME | STREAM |
| M001 | JAYA | SCIENCE |
| M002 | ADITYA | HUMANITIES |
| M003 | HANSRAJ | SCIENCE |
| M004 | SHIVAK | COMMERCE |
RESULT
| NO | MNAME | STREAM |
| M002 | ADI'l'YA | HUMANITIES |
Concept: Structured Query Language Advantages of Using SQL
Write SQL queries for (i) to (iv) and find outputs for SQL queries (v) to (viii), which are based on the tables.
DVD
| DCODE | DTITLE | DTYPE |
| F101 | Henry Martin | Folk |
| C102 | Dhrupad | Classical |
| C101 | The Planets | Classical |
| F102 | Universal Soldier | Folk |
| R102 | A day in life | Rock |
MEMBER
| MID | NAME | DCODE | ISSUEDATE |
| 101 | AGAM SINGH | R102 | 2017-11-30 |
| 103 | ARTH JOSEPH | F102 | 2016-12-13 |
| 102 | NISHA HANS | C101 | 2017-07- 24 |
1) To display all details from the table MEMBER in descending order of ISSUEDATE
2) To display the DCODE and DTITLE of all Folk Type DVDs from the table DVD.
3) To display the DTYPE and number of DVDs in each DTYPE from the table DVD.
4) To display all NAME and ISSUEDATE of those members from the table. MEMBER who have DVDs issued (i.e., ISSUEDATE) in the year 2017
5) SELECT MIN(ISSUEDATE) FROM MEMBER
6) SELECT DISTINCT DTYPE FROM DVD;
7) SELECT D.DCODE, NAME, DTITLE FROM DVD D, MEMBER M WHERE D.DCODE=M.DCODE;
8) SELECT DTITLE FROM DVD WHERE DTYPE NOT IN ("Folk", "Classical" ) ;
Concept: Structured Query Language Advantages of Using SQL
Observe the following table carefully and· write the names of the most appropriate columns, which can be considered as (i) candidate keys and. (ii) primary key:
| Code | Item | Qty | Price | Transaction Date |
| 1001 | Plastic Folder 14" | 100 | 3400 | 2014-12-14 |
| 1004 | Pen Stand Standard | 200 | 4500 | 2015-01-31 |
| 1005 | Stapler Mini | 250 | 1200 | 2015-02-28 |
| 1009 | Punching Machine Small | 200 | 1400 | 2015-03-12 |
| 1003 | Stapler Big | 100 | 1500 | 2015-02-02 |
Concept: Introduction to Data Base Concepts and Its Need in C++
Consider the following DEPT and EMPLOYEE tables. Write SQL queries for (i) to (iv) and find outputs for SQL queries (v) to (viii).
Table: DEPT
| DCODE | DEPARTMENT | LOCATION |
| D01 | INFRASTRUCTURE | DELHI |
| D02 | MARKETING | DELHI |
| D03 | MEDIA | MUMBAI |
| D04 | FINANCE | KOLKATA |
| D05 | HUMAN RESOURCE | MUMBAI |
Table: EMPLOYEE
| ENO | NAME | DOJ | DOB | GENDER | DCODE |
| 1001 | George K | 2013-09-02 | 1991-09-01 | MALE | D01 |
| 1002 | Ryma Sen | 2012-12-11 | 1990-12-15 | FEMALE | D03 |
| 1003 | Mohitesh | 2013-02-03 | 1987-09--04 | MALE | D05 |
| 1007 | Anil Jha | 2014-01-17 | 1984-10-19 | MALE | D04 |
| 1004 | Manila Sahai | 2012-12-09 | 1986-11-14 | FEMALE | D01 |
| 1005 | R SAHAY | 2013-11-18 | 1987-03-31 | MALE | D02 |
| 1006 | Jaya Priya | 2014-06-09 | 1985-06-23 | FEMALE | D05 |
Note: DOJ refers to the date of joining ·and DOB refers to the date of Birth of employees
1) To display Eno, Name, Gender from the table EMPLOYEE in ascending order of Eno.
2) To display the Name of all the MALE Employees from the table EMPLOYEE.
3) To display the Eno and Name of those employees from the table EMPLOYEE who are born between '1987-01-01' and '1991-12-01'.
4) To count and display FEMALE employees who have Joined after '1986-01-01'.
5) SELECT COUNT(*), DCODE FROM EMPLOYEE GROUP BY DCODE HAVING COUNT(*)>1;
6) SELECT DISTINCT DEPARTMENT FROM DEPT;
7) SELECT NAME, DEPARTMENT FROM EMPLOYEE E, DEPT D WHERE E.DCODE=D.DCODE AND EN0<1003;
8) SELECT MAX(DOJ), MIN(DOB) FROM EMPLOYEE;
Concept: Structured Query Language Advantages of Using SQL
State any one Absorption Law of Boolean Algebra and verily it using truth table.
Concept: Truth Tables (Boolean Algebra)
Draw the Logic Circuit of the following Boolean Expression
(U' + v).(V' + W')
Concept: Application of Boolean Logic - Digital Electronic Circuit Design Using Basic Logic Gates (NOT, AND, OR, NAND, NOR)
Derive a Canonical POS expression for a Boolean function FN, represented by the following truth truth table:
| X | y | z | FN (X, Y, Z) |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Concept: Obtaining Sum of Product (SOP) and Product of Sum (POS) Form the Truth Table
Reduce the following Boolean Expression to its simplest form using K-Map:
`G(U, V,W, Z) = sum(3,5 , 6 , 7 , 11 , 12 ,13, 15)`
Concept: Reducing Boolean Expression (SOP and POS) to Its Minimal Form
State DeMorgan's Laws of Boolean Algebra and verify them using a truth table.
Concept: DeMorgan’S Law/Theorem and Their Applications
Draw the Logic Circuit of the following Boolean Expression using only NOR Gates
(A+B).(C+D)
Concept: Application of Boolean Logic - Digital Electronic Circuit Design Using Basic Logic Gates (NOT, AND, OR, NAND, NOR)
Derive a Canonical POS expression for a Boolean function G, represented by the following truth table:
| X | Y | Z | G(X, Y, Z) |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Concept: Obtaining Sum of Product (SOP) and Product of Sum (POS) Form the Truth Table
