Advertisements
Advertisements
Give the scientific term for the following:
Multiple effects of a gene on the phenotype of an organism.
Concept: Extensions of Mendelian Genetics (Deviation from Mendelism)
Explain Pleiotropy with reference to phenylketonuria.
Concept: Extensions of Mendelian Genetics (Deviation from Mendelism)
A homozygous pea plant with round seed coat and yellow cotyledons are crossed with another homozygous, pea plant having wrinkled seed coat and green cotyledons.
(i) Give the types of gametes produced by plants of F-generation.
(ii) Give the dihybrid phenotypic ratio with the corresponding phenotypes.
(iii) State Mendel’s principle involved in this cross.
Concept: Heredity and Variation
Mention one cause for variation in nature.
Concept: Heredity and Variation
Explain the process of sex determination in honey bees.
Concept: Sex Determination > Sex Determination in Honey Bees
Define complete linkage. Give an example of a cross, showing complete linkage.
Concept: Linkage and Crossing Over
Give an account of artificial chromosomes in the transfer of genetic material.
Concept: Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance
The maternal grandfather of a boy is colorblind, but his maternal grandmother is normal. The father of the boy is also normal. What is the probability of this boy being colorblind?
Concept: Mendelian Inheritance - Mendel’s Law of Heredity
The pedigree chart given below represents the pattern of inheritance of sickle cell anemia in a family. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow.

- What is the genotype of the father?
- What is the phenotype of the mother?
Concept: Extensions of Mendelian Genetics (Deviation from Mendelism) > Polygenic Inheritance
Explain the process of sex determination in Grasshopper.
Concept: Sex Determination > Sex Determination in Some Insects
What is the genotype of Turner's Syndrome?
Concept: Genetic Disorders
Mention any one symptom of Turner's syndrome.
Concept: Genetic Disorders
Four triplet codons code for the amino acid valine. Three of them are given below.
GUU GUC GUA
Write the fourth codon.
Concept: Extensions of Mendelian Genetics (Deviation from Mendelism)
A haemophilic man marries a carrier woman and they have a daughter. What is the probability of their daughter being haemophilic?
Concept: Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance
The pedigree chart given below represents the pattern of inheritance of thalassemia in a family.
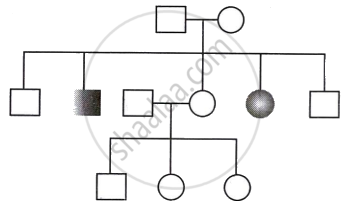
What could be the genotype of the affected male?
Concept: Extensions of Mendelian Genetics (Deviation from Mendelism) > Polygenic Inheritance
In a karyotype analysis, X and Y chromosomes represent sex chromosomes.
Name the scientist who discovered the X chromosome.
Concept: Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance
Jacob is genetically a carrier of the disorder that affects the shape of the RBCs, as shown in the diagram below. His son James suffers from the same disorder.

- Give the biochemical reason for the disorder that changes the shape of the RBCs, as shown above.
- Draw a Punnett square to show the genotype of the mother of James.
- Name and define the type of 'point mutation' responsible for this disorder.
Concept: Genetic Disorders
A male plant bearing red flowers was crossed with a female plant bearing yellow flowers. In the F1 generation, all the flowers were orange in colour.
Mention the ratio of red flowers, yellow flowers and orange flowers in the F2 generation.
Concept: Mendelian Inheritance - Mendel’s Law of Heredity
Tall pea plants having green pods were crossed with dwarf pea plants having yellow pods. Out of 80 plants, how many are likely to be tall plants in the F2 generation?
Concept: Mendelian Inheritance - Mendel’s Law of Heredity
Consider the following information and answer the question that follows:
|
Make a single pedigree chart using the above information to show the pattern of inheritance of phenylketonuria (PKU) in the family of Reshma.
Concept: Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance
