Advertisements
Advertisements
A homogeneous cylinder 3 m diameter and weighing 400 N is resting on two rough inclined surface’s shown.If the angle of friction is 15o.Find couple C applied to the cylinder that will start it rotating clockwise.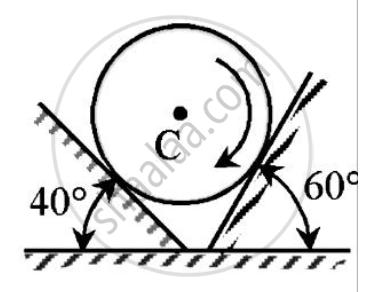
Concept: Cone of Friction
The system in figure is initially at rest.
Neglecting friction determine the force P required if the velocity of the collar is 5 m/s after 2 sec and corresponding tension in the cable.
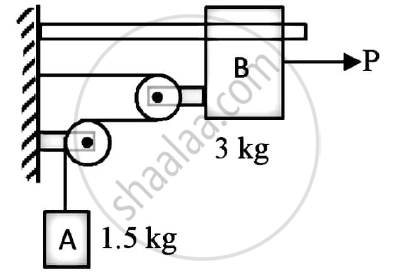
Concept: Introduction to Laws of Friction
Find the force ‘F’ to have motion of block A impeding up the plane. Take coefficient of friction for all the surfaces in contact as 0.2. Consider the wedge B as weightless. Refer Figure 11.
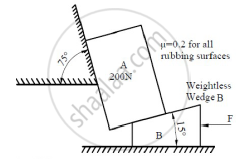
Concept: Application to Problems Involving Wedges
Find the weight WB so as to have its impending motion down the plane. Take weight of block A as 2kN. The pin connected rod AB is initially is in horizontal position. Refer Figure 13. Coefficient of friction = 0.25 for all surfaces.

Concept: Cone of Friction
Determine the tension in a cable BC shown in fig by virtual work method.

Given: F=3500 N
ϴ = 50o
Length of rod = 3.75 mm + 1.5 mm = 5.25 mm
To find : Tension in cable BC
Concept: Applications on Equilibrium Mechanisms
Two cylinders 1 and 2 are connected by a rigid bar of negligible weight hinged to each cylinder and left to rest in equilibrium in the position shown under the application of force P applied at the center of cylinder 2.
Determine the magnitude of force P.If the weights of the cylinders 1 and 2 are 100N and 50 N respectively.
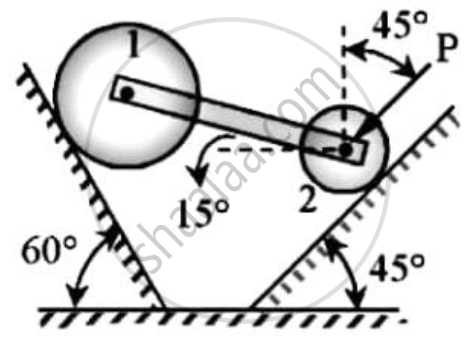
Concept: Applications on Equilibrium Mechanisms
Determine the required stiffness k so that the uniform 7 kg bar AC is in equilibrium when θ=30o.
Due to the collar guide at B the spring remains vertical and is unstretched when θ = 0o.Use principle of virtual work.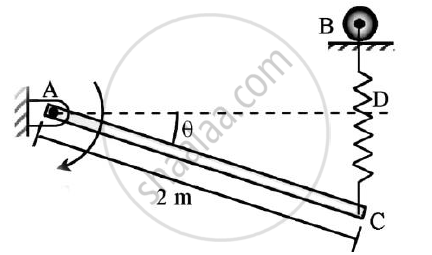
Concept: Applications on Equilibrium Mechanisms
Using Principle of Virtual Work, determine the force P which will keep the weightless bar AB in equilibrium. Take length AB as 2m and length AC as 8m. The bar makes an angle of 30° with horizontal. All the surfaces in contact are smooth. Refer Figure 9.
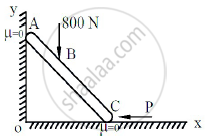
Concept: Applications on Equilibrium Mechanisms
Find the co-ordinate of the centroid of the area as shown in the given figure.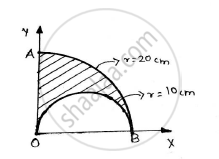
Concept: Velocity and Acceleration in Terms of Rectangular Co-ordinate System
The position vector of a particle which moves in the X-Y plane is given by 𝒓̅ = (3t3-4t2)𝒊̅ + (0.5t4)𝒋̅
Concept: Velocity and Acceleration in Terms of Rectangular Co-ordinate System
Two balls having 20kg and 30 kg masses are moving towards each other with velocities of 10 m/s and 5 m/s respectively as shown in the figure.
If after the impact ,the ball having 30 kg mass is moving with 6 m/s velocity to the right then determine the coefficient of restitution between the two balls.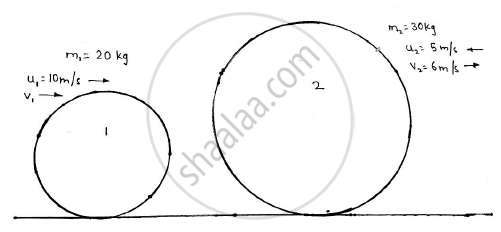
Concept: Velocity and Acceleration in Terms of Rectangular Co-ordinate System
The V-X graph of a rectilinear moving particle is shown. Find the acceleration of the particle at 20m,80 m and 200 m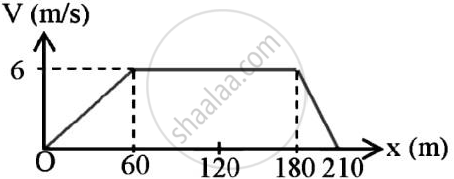
Concept: Velocity and Acceleration in Terms of Rectangular Co-ordinate System
A bar 2 m long slides down the plane as shown.The end A slides on the horizontal floor with a velocity of 3 m/s.Determine the angular velocity of rod AB and the velocity of end B for the position shown.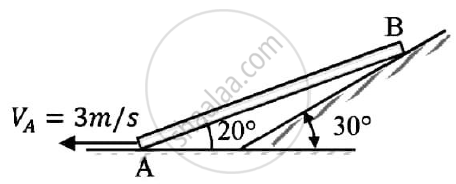
Concept: Velocity and Acceleration in Terms of Rectangular Co-ordinate System
A 500 N Crate kept on the top of a 15° sloping surface is pushed down the plane with an initial velocity of 20m/s. If μs = 0.5 and μk = 0.4, determine the distance travelled by the block and the time it will take as it comes to rest.
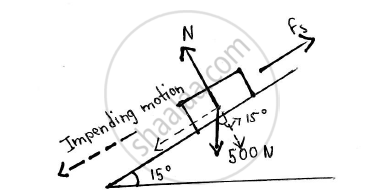
Given: Weight of crate = 500 N
Initial velocity(u) = 20 m/s
μs = 0.5
μk = 0.4
θ = 15°
Final velocity (v) = 0 m/s
To find: Distance travelled by the block Time it will take before coming to rest
Concept: Velocity and Acceleration in Terms of Rectangular Co-ordinate System
Derive the equation of path of a projectile and hence show that equation of path of projectile is a parabolic curve.
Concept: Velocity and Acceleration in Terms of Rectangular Co-ordinate System
particle is moving in X-Y plane and it’s position is defined by`bar r=(3/2 t^2)bar l+(2/3 t^3) barJ "Find radius of curvature when t=2sec." `
Concept: Velocity and Acceleration in Terms of Rectangular Co-ordinate System
A Force of 100 N acts at a point P(-2,3,5)m has its line of action passing through Q(10,3,4)m. Calculate moment of this force about origin (0,0,0).
Concept: Velocity and Acceleration in Terms of Rectangular Co-ordinate System
From (v-t) diagram find (1) Distance travelled in 10 second.
(2) Total distance travelled in 50 second.
(3) Retardation
Concept: Motion Curves (a-t, v-t, s-t curves)
Blocks P1 and P2 are connected by inextensible string.Find velocity of block P1,if it falls by 0.6 m starting from rest.
The co-efficient of friction is 0.2.The pulley is frictionless.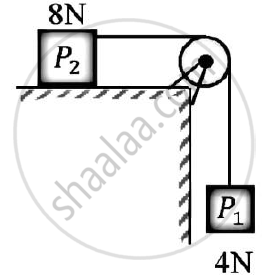
Concept: Velocity and Acceleration in Terms of Rectangular Co-ordinate System
Co-ordinate distance are in m units for the space frame in figure.
There are 3 members AB,AC and AD.There is a force W=10 kN acting at A in a vertically upward direction.
Determine the tension in AB,AC and AD.

Concept: Velocity and Acceleration in Terms of Rectangular Co-ordinate System
