Advertisements
Chapters
2: The Sun, the Moon and the Earth
3: Tides
4: Air Pressure
▶ 5: Winds
6: Natural Regions
7: Soils
8: How Seasons Occur - Part 2
9: Agriculture
10: Human Settlements
11: Contour Maps and Landforms
![Balbharati solutions for Geography (Social Science) [English] 7 Standard chapter 5 - Winds Balbharati solutions for Geography (Social Science) [English] 7 Standard chapter 5 - Winds - Shaalaa.com](/images/geography-social-science-english-7-standard_6:f92fa167f106463d84bcfc1440408f8d.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 5: Winds
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 5 of Maharashtra State Board Balbharati for Geography (Social Science) [English] 7 Standard.
Balbharati solutions for Geography (Social Science) [English] 7 Standard 5 Winds Exercises [Pages 28 - 29]
When the air expands, it _____.
becomes solid
becomes thinner
gets lost
becomes humid
From high air pressure regions, winds ______.
blow to regions of still higher pressure.
blow towards regions of cooler air.
blow towards regions of low air pressure.
remain still.
In the northern hemisphere, winds blowing towards the equator ______ due to the rotation of the earth.
turn to the south
turn to the east
turn to the west
turn to the north
The direction of seasonal winds blowing over the Indian subcontinent during winter is from the ______.
south-east to north-west.
south-west towards north-east.
north-east to south-west.
north-west to south-east.
The Roaring Forties in the southern hemisphere ______.
blow towards the equator
blow in the areas around 40° S parallel
blow from the subpolar region of low pressure.
blow around 40° N parallel.
Identify the type of wind from the description given below.
These winds from the south-west bring rains to the Indian subcontinent. During June to September, India gets rains. After this period, these winds retreat.
Identify the type of wind from the description given below.
These winds blowing from the north pole region towards 60° N parallel cause cold wave conditions in extensive areas covering North America, Europe, and Russia.
Identify the type of wind from the description given below.
Hilltops get heated quickly during the day. The air in this part becomes hot, light, and starts ascending. Hence, a low-pressure area forms in this region. At the same time, the air at the foothills being cooler, and that area experiences high pressure. The air in that area blows towards low pressure.
Given below are the values of air pressure in millibars. Using the same, draw a diagram to show a cyclone and an anticyclone.
990, 994, 996, 1000
Given below are the values of air pressure in millibars. Using the same, draw a diagram to show a cyclone and an anticyclone.
1030, 1020, 1010, 1000
State one reason why.
A belt of calm exists near the equator.
State one reason why.
The winds coming from the north-west in the southern hemisphere have greater velocities than the winds coming from the south-west in the northern hemisphere.
State one reason why.
The monsoon winds in the summer come from the sea but the retreating monsoon winds in winter come from the land.
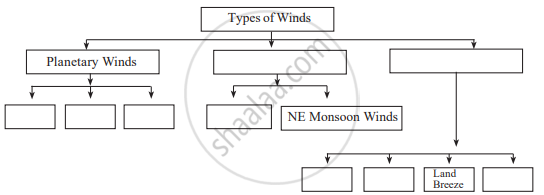
Complete the flow chart:
Why is the air pressure high in polar areas in both the hemispheres?
What effect does the rotation of the earth have on the winds?
Why do the cyclonic winds blow in a circular manner?
State the reasons that lead to the formation of cyclones and describe the effects of cyclones.
Solutions for 5: Winds
![Balbharati solutions for Geography (Social Science) [English] 7 Standard chapter 5 - Winds Balbharati solutions for Geography (Social Science) [English] 7 Standard chapter 5 - Winds - Shaalaa.com](/images/geography-social-science-english-7-standard_6:f92fa167f106463d84bcfc1440408f8d.jpg)
Balbharati solutions for Geography (Social Science) [English] 7 Standard chapter 5 - Winds
Shaalaa.com has the Maharashtra State Board Mathematics Geography (Social Science) [English] 7 Standard Maharashtra State Board solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Balbharati solutions for Mathematics Geography (Social Science) [English] 7 Standard Maharashtra State Board 5 (Winds) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Balbharati textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Geography (Social Science) [English] 7 Standard chapter 5 Winds are Planetary Winds, Local Winds, Characteristics of Valley Breeze, Characteristics of the Mountain Breeze, Seasonal Winds (Monsoon), Cyclones, Cyclonic Storms, Wind: The Movement of Air, Anticyclones.
Using Balbharati Geography (Social Science) [English] 7 Standard solutions Winds exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Balbharati Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum Maharashtra State Board Geography (Social Science) [English] 7 Standard students prefer Balbharati Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 5, Winds Geography (Social Science) [English] 7 Standard additional questions for Mathematics Geography (Social Science) [English] 7 Standard Maharashtra State Board, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
