Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
1: The First War of Independence, 1857
2: Growth of Nationalism
3: First Phase of the Indian National Movement
4: Second Phase of the Indian National Movement
5: The Muslim League
II. MASS PHASE OF THE NATIONAL MOVEMENT (1915-1947)
6: Mahatma Gandhi and the National Movement
7: Quit India Movement
8: Forward Bloc and The INA
▶ 9: Independence and Partition of India
III. THE CONTEMPORARY WORLD
10: The First World War
11: Rise of Dictatorships
12: The Second World War
13: United Nations
14: Major Agencies of the United Nations
15: Non-Aligned Movement
SECTION B - CIVICS : I. THE UNION LEGISLATURE
1: The Union Parliament
II. THE UNION EXECUTIVE
2: The President and The Vice-President
3: Prime Minister and Council of Ministers
III. THE JUDICIARY
4: The Supreme Court
5: The High Courts and Subordinate Courts
![Morning Star solutions for Total History and Civics [English] Class 10 chapter 9 - Independence and Partition of India Morning Star solutions for Total History and Civics [English] Class 10 chapter 9 - Independence and Partition of India - Shaalaa.com](/images/total-history-and-civics-english-class-10_6:f32d3458d7ba4c159209b7405ae151c7.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 9: Independence and Partition of India
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 9 of CISCE Morning Star for Total History and Civics [English] Class 10.
Morning Star solutions for Total History and Civics [English] Class 10 9 Independence and Partition of India Exercises [Pages 110 - 113]
Multiple-Choice Questions
Which of the following international events forced Britain to consider handing over the governance of India to Indians?
End of Fascism
Rise of Communism
World War II
Rise of USA as a Superpower
Who among the following was NOT a part of the Cabinet Mission?
Penthic Lawrence
Sir Stafford Cripps
A.V. Alexander
Lord Linlithgow
Arrange the following events in chronological order:
- End of World War
- Attlee's Announcement
- Mountbatten Plan
- Cabinet Mission
(i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(i), (iv), (ii) , and (iii)
(i), (iv), (iii) and (ii)
(i), (iii), (ii) and (iv)
Why was the Cabinet Mission sent to India in 1946?
To facilitate transfer of power to Indians
To facilitate the Partition of the country
To facilitate the division of resources between Provinces and Princely States.
To facilitate the drawing up of the Constitution for each Dominion.
Group A : United Provincess : : Group B : ______
Baluchistan
Punjab
Delhi
Bihar
Which of the following was NOT proposed by the Cabinet Mission?
Federal Union of British Provinces
Formation of a Constituent Assembly
British Provincess to be divided on linguistic basis
Union government would control communication
Why did the Muslim League accept the Cabinet Mission Plan?
Its demand for a separate nation was fulfilled.
It felt that grouping of Muslim majority Provinces was a step towards a separate dominion.
It felt that its claim to nominate Muslim members to the Executive Council was supported.
None of the above.
Which of the following is incorrect about the formation of a Constituent Assembly according to the Cabinet Mission Plan?
Members to be directly elected by the people of India
Members to be elected by Provincial Legislative Assemblies
296 members from the Provinces and 93 from princely states
Complete freedom to frame the Constitution of the Indian Union
Which of the following forced the British government to send Lord Mountbatten?
Communal riots
Labour Unrest
Congress-League deadlock
All of the above
The Muslim League put forth a demand which had tragic consequences. What was the demand? What did it result in?
The demand for a separate Muslim-dominated Pakistan: It resulted in the Partition of country.
The demand for separate electorate for Muslims. It resulted in the Partition of India.
The demand for Muslim leadership of the country. It resulted in the formation of Pakistan.
The demand to have a Governor General of a dominion. It resulted in the Partition of the country.
According to Indian Independence Act, a plebiscite would be held in ______.
Bihar
Sylhet
Princely states
Central provinces
According to Mountbatten Plan which is incorrect regarding the status of Princely States?
They will become independent
All treaties would end
Plebiscite will be held
Freedom to associate with any dominion
The Indian Independence Act provided for division of which state if so desired by the people?
Jammu and Kashmir
Punjab and Bengal
Bihar and Orissa (Odisha)
Bombay and Madras
Which of the following provisions regarding the Constituent Assemblies is/are correct?
Act as Central Legislatures in each dominion
Full powers to make laws for their dominion
Act as soverign bodies for legislative purpose
All of the above
Who had the power to bring India Independence Act into operation?
The Secretary of State for India
The Governor General
The British Prime Minister
None of the above
Short Answer Questions
State two important reasons that prompted the British to withdraw from India.
In what way did the outcome of the Second World War help India’s demand for self-Govemment?
What was the implication of the Group 'B' States proposed by the Cabinet Mission Plan?
What was mentioned in the Cabinet Mission Plan regarding provincial Autonomy?
What arguments did the Cabinet Mission give to reject Jinnah's proposal of Pakistan?
What was said in the Cabinet Mission Plan about the division of power between the Federal Government and the Provinces?
Why did the Muslim League accept Cabinet Mission proposals?
What was the reactions of the Congress to the Cabinet Mission Plan.
Who was elected as the President of the Constituent Assembly in 1946?
Name the last Viceroy of India.
State one proposal regarding the Princely States made by the last Viceroy of India.
What was the most important but tragic provision of the Mountbatten Plan?
To whom was the power to be transferred according to the Mountbatten Plan?
Mention the reasons that‘made the Congress accept the Partition Proposals.
Mention any two provisions of the Indian Independence Act, 1947.
What did the Indian Independence Act 1947 state about Bengal and Punjab?
What did the Indian Independence Act 1947 state about North West Frontier Province?
What did the Indian Independence Act 1947 state about Sylhet District of Assam?
Name the first Governor-General of independent India.
Name the first Indian Governor-General of India.
Structured Questions
The Cabinet Mission Plan proposed a two-tiered federal union of British Provinces and Princely States. With reference to this, describe the following:
- Name the persons who constituted the Cabinet Mission. What was the purpose of sending the Cabinet Mission to India in 1946?
- The federal structure proposed by the Cabinet Mission Plan.
- The option given to the Princely States.
The attempt of the British to pacify the Congress and the Muslim League was clearly visible in the Cabinet Mission proposals but in reality neither could be pleased. With reference to this, explain:
- Any three proposals of the Cabinet Mission.
- The reasons for the Muslim League's acceptance and later rejection of the Cabinet Mission Plan.
- Why did the Congress refuse to participate in the formation of the Interim Government under the Cabinet Mission Plari?
Picture Study
In the historic photograph, Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru, is being sworn in as Prime Minister of free India. In this context answer the following: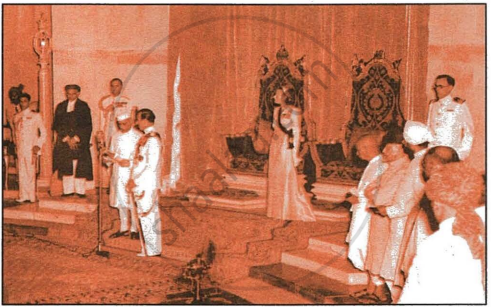
- Mention the Provisions of the Indian Independence Act of 1947 regarding the Constituent Assembly.
- Discuss the basic reasons why the Cabinet Mission Plan rejected the demand for Pakistan.
- Mention the areas where plebiscites were to be held. What was the position of His Majesty's government in the new set-up in India?
With reference to the given picture answer the questions that follow:

- Identify the person in the picture. State any two features of the Plan devised by him.
- How did he plan to solve the communal problem existing in India?
- Why did the Congress accept the Plan? State three reasons to justify its acceptance.
Thinking Skills
A number of Acts were passed by the British to pacify the demands of the Indians relating to the Government of India. But the Indian Independence Act, 1947 is considered as a unique piece of legislation. Why is it so? Give reasons to support your answer.
Do you think that the Congress had no alternative but to accept the Mountbatten Plan? Support your answer with examples.
Solutions for 9: Independence and Partition of India
![Morning Star solutions for Total History and Civics [English] Class 10 chapter 9 - Independence and Partition of India Morning Star solutions for Total History and Civics [English] Class 10 chapter 9 - Independence and Partition of India - Shaalaa.com](/images/total-history-and-civics-english-class-10_6:f32d3458d7ba4c159209b7405ae151c7.jpg)
Morning Star solutions for Total History and Civics [English] Class 10 chapter 9 - Independence and Partition of India
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Total History and Civics [English] Class 10 CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Morning Star solutions for Mathematics Total History and Civics [English] Class 10 CISCE 9 (Independence and Partition of India) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Morning Star textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Total History and Civics [English] Class 10 chapter 9 Independence and Partition of India are Clauses of Cabinet Mission Plan, Mountbatten Plan (Clauses and Its Acceptance), Indian Independence Act of 1947, Independence by an Act of Legislation, Events that Led to the Cabinet Mission, Cabinet Mission in India, Rejection of the Demand for Pakistan, Reaction to the Cabinet Mission Plan, Conflict Between Congress and Muslim League.
Using Morning Star Total History and Civics [English] Class 10 solutions Independence and Partition of India exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Morning Star Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Total History and Civics [English] Class 10 students prefer Morning Star Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 9, Independence and Partition of India Total History and Civics [English] Class 10 additional questions for Mathematics Total History and Civics [English] Class 10 CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
