Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
▶ 2: Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
3: Human Reproduction
4: Reproductive Health
5: Principle of Inheritance and Variation
6: Molecular Basis of Inheritance
7: Evolution
8: Human Health and Diseases
9: Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production
10: Microbes in Human Welfare
11: Biotechnology : Principles and Processes
12: Biotechnology and Its Applications
13: Organisms and Populations
14: Ecosystem
15: Biodiversity and Conservation
16: Environmental Issues
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 12 chapter 2 - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 12 chapter 2 - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - Shaalaa.com](/images/biology-english-class-12_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 2: Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 2 of CBSE NCERT Exemplar for Biology [English] Class 12.
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 12 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS [Pages 9 - 12]
Among the terms listed below, those that of are not technically correct names for a floral whorl are:
- Androecium
- Carpel
- Corolla
- Sepal
ii and iv
i and ii
iii and iv
i and iv
Embryo sac is to ovule as ______ is to an anther.
Pollen grain
Androecium
Filament
Stamen
In a typical complete, bisexual, and hypogynous flower the arrangement of floral whorls on the thalamus from the outermost to the innermost is ______.
Calyx, corolla, androecium, and gynoecium
Calyx, corolla, gynoecium and androecium
Gynoecium, androecium, corolla and calyx
Androecium, gynoecium, corolla and calyx
A dicotyledonous plant bears flowers but never produces fruits and seeds. The most probable cause for the above situation is ______.
Plant is dioecious and bears only staminate flowers
Plant is monoecious
Plant is dioecious and bears both pistillate and staminate flowers
Plant is dioecious and bears only pistillate flowers
The outermost and innermost wall layers of microsporangium in an anther are respectively ______.
Epidermis and tapetum
Epidermis and middle layer
Epidermis and endodermis
Endothecium and tapetum
During microsporogenesis, meiosis occurs in ______.
Microspore mother cells
Microspore tetrads
Pollen grains
Endothecium
From among the sets of terms given below, identify those that are associated with the gynoecium.
Stigma, ovule, embryo sac, placenta
Thalamus, pistil, style, ovule
Ovule, ovary, embryo sac, tapetum
Ovule, stamen, ovary, embryo sac
Starting from the innermost part, the correct sequence of parts in an ovule are ______.
egg, embryo sac, nucellus, integument
embryo sac, nucellus, integument, egg
egg, integument, embryo sac, nucellus
egg, nucellus, embryo sac, integument
From the statements given below choose the option that are true for a typical female gametophyte of a flowering plant.
- It is 8-nucleate and 7-celled at maturity
- It is free-nuclear during the development
- It is situated inside the integument but outside the nucellus
- It has an egg apparatus situated at the chalazal end
i and ii
ii and iv
i and iv
None of these
Autogamy can occur in a chasmogamous flower if ______.
Pollen matures before maturity of ovule
Ovules mature before maturity of pollen
Both pollen and ovules mature simultaneously
Both anther and stigma are of equal lengths.
Choose the correct statement from the following:
Cleistogamous flowers always exhibit autogamy
Chasmogamous flowers always exhibit geitonogamy
Cleistogamous flowers exhibit both autogamy and geitonogamy
Chasmogamous flowers never exhibit autogamy
A particular species of plant produces light, non-sticky pollen in large numbers and its stigmas are long and feathery. These modifications facilitate pollination by ______.
Wind
Animals
Water
Insects
From among the situations given below, choose the one that prevents both autogamy and geitonogamy.
Monoecious plant bearing unisexual flowers
Dioecious plant bearing only male or female flowers
Monoecious plant with bisexual flowers
Dioecious plant with bisexual flowers
In a fertilised embryo sac, the haploid, diploid, and triploid structures are ______.
Synergid, zygote, and primary endosperm nucleus
Synergid, antipodal and polar nuclei
Antipodal, synergid, and primary endosperm nucleus
Synergid, polar nuclei and zygote
In an embryo sac, the cells that degenerate after fertilisation are ______.
Synergids and primary endosperm cell
Synergids and antipodals
Antipodals and primary endosperm cell
Egg and antipodals
While planning for an artificial hybridization programme involving dioecious plants, which of the following steps would not be relevant ______.
Emasculation
Collection of pollen
Dusting of pollen on stigma
Bagging of female flower
In the embryos of a typical dicot and a grass, true homologous structures are ______.
Coleorhiza and coleoptile
Coleoptile and scutellum
Cotyledons and scutellum
Hypocotyl and radicle
The phenomenon observed in some plants wherein parts of the sexual apparatus are used for forming embryos without fertilization is called ______
parthenocarpy
apomixis
vegetative propagation
sexual reproduction
In a flower, if the megaspore mother cell forms megaspores without undergoing meiosis and if one of the megaspores develops into an embryo sac, its nuclei would be ______.
Haploid
Diploid
A few haploid and a few diploid
With varying ploidy
The phenomenon wherein, the ovary develops into a fruit without fertilisation is called ______.
Parthenocarpy
Apomixis
Asexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 12 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants VERY SHORT ANSWER [Pages 12 - 14]
Name the component cells of the ‘egg apparatus’ in an embryo sac.
Name the part of gynoecium that determines the compatible nature of pollen.
Name the common function that cotyledons and nucellus perform.
Complete the following flow chart

Indicate the stages where meiosis and mitosis occur (1, 2 or 3) in the flow chart.
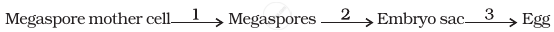
In the diagram given below, show the path of a pollen tube from the pollen on the stigma into the embryo sac. Name the components of egg apparatus.
Name the parts of pistil which develop into fruit and seeds.
In case of polyembryony, if an embryo develops from the synergid and another from the nucellus which is haploid and which is diploid?
Can an unfertilised, apomictic embryo sac give rise to a diploid embryo? If yes, then how?
Which are the three cells found in a pollen grain when it is shed at the three celled stage?
What is self-incompatibility?
Name the type of pollination in self-incompatible plants.
Draw the diagram of a mature embryo sac and show its 8-nucleate, 7-celled nature. Show the following parts: antipodals, synergids, egg, central cell, polar nuclei.
Which is the triploid tissue in a fertilised ovule? How is the triploid condition achieved?
Are pollination and fertilisation necessary in apomixis? Give reasons.
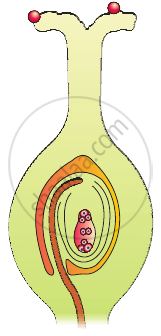
Identify the type of carpel with the help of diagrams given below:
How is pollination carried out in water plants?
What is the function of the two male gametes produced by each pollen grain in angiosperms?
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 12 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants SHORT ANSWER [Pages 14 - 16]
List three strategies that a bisexual chasmogamous flower can evolve to prevent self pollination (autogamy).
Given below are the events that are observed in an artificial hybridization programme. Arrange them in the correct sequential order in which they are followed in the hybridisation programme.
(a) Re-bagging;
(b) Selection of parents;
(c) Bagging;
(d) Dusting the pollen on stigma;
(e) Emasculation;
(f) Collection of pollen from male parent.
Vivipary automatically limits the number of offsprings in a litter. How?
Does self incompatibility impose any restrictions on autogamy? Give reasons and suggest the method of pollination in such plants.
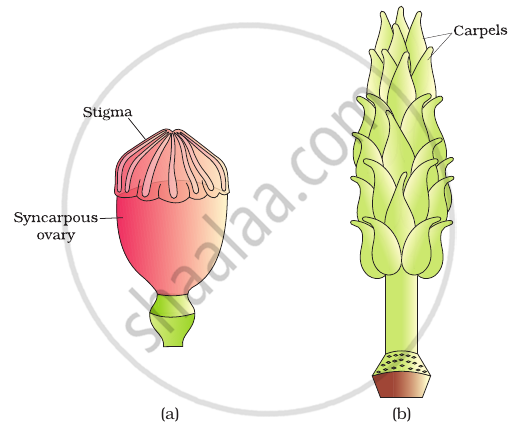
In the given diagram, write the names of parts shown with lines.
What is polyembryony and how can it be commercially exploited?
Are parthenocarpy and apomixis different phenomena? Discuss their benefits.
Why does the zygote begin to divide only after the division of Primary endosperm cell (PEC)?
The generative cell of a two-celled pollen divides in the pollen tube but not in a three-celled pollen. Give reasons.
In the figure given below label the following parts: male gametes, egg cell, polar nuclei, synergid and pollen tube
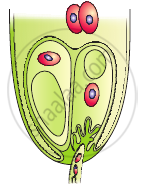
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 12 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants LONG ANSWER [Page 16]
Starting with the zygote, draw the diagrams of the different stages of embryo development in a dicot.
What are the possible types of pollinations in chasmogamous flowers. Give reasons.
With a neat, labelled diagram, describe the parts of a mature angiosperm embryo sac. Mention the role of synergids.
Draw the diagram of a microsporangium and label its wall layers. Write briefly on the role of the endothecium.
Embryo sacs of some apomictic species appear normal but contain diploid cells. Suggest a suitable explanation for the condition.
Solutions for 2: Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 12 chapter 2 - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 12 chapter 2 - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - Shaalaa.com](/images/biology-english-class-12_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 12 chapter 2 - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Biology [English] Class 12 CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics Biology [English] Class 12 CBSE 2 (Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT Exemplar textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Biology [English] Class 12 chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants are Flower - a Fascinating Organ of Angiosperms, Pollination, Essential Parts of Flower: Androecium, Essential Parts of Flower: Gynoecium, Fertilization Process, Artificial Hybridization, Post Fertilization in Plant: Development of Embryo (Embryogeny), Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants, Outbreeding Devices, Kinds of Pollination, Agents of Pollination, Development of Endosperm, Development of Seed, Development of Fruit, Polyembryony, Parts of Flower, Accessory Organs, Pre-fertilisation in Flowering Plant: Structures and Events, Development of Anther, Transverse Section of Mature Anther (Microsporangium), Microsporogenesis, Microspores and Pollen Grains, Development of Male Gametophyte, Advantages and Disadvantages of Pollen Grains, Structure of Ovule (Megasporangium), Types of Ovules, Megasporogenesis, Development of Female Gametophyte or Embryo Sac, Self Pollination (Autogamy), Cross Pollination, Abiotic Agents, Biotic Agents, Post Fertilisation in Plant: Structures and Events, Apomixis, Fertilization Process.
Using NCERT Exemplar Biology [English] Class 12 solutions Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Exemplar Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Biology [English] Class 12 students prefer NCERT Exemplar Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 2, Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Biology [English] Class 12 additional questions for Mathematics Biology [English] Class 12 CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
