Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
3: Human Reproduction
4: Reproductive Health
▶ 5: Principle of Inheritance and Variation
6: Molecular Basis of Inheritance
7: Evolution
8: Human Health and Diseases
9: Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production
10: Microbes in Human Welfare
11: Biotechnology : Principles and Processes
12: Biotechnology and Its Applications
13: Organisms and Populations
14: Ecosystem
15: Biodiversity and Conservation
16: Environmental Issues
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 12 chapter 5 - Principle of Inheritance and Variation NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 12 chapter 5 - Principle of Inheritance and Variation - Shaalaa.com](/images/biology-english-class-12_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 5: Principle of Inheritance and Variation
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 5 of CBSE NCERT Exemplar for Biology [English] Class 12.
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 12 5 Principle of Inheritance and Variation MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS [Pages 29 - 32]
All genes located on the same chromosome ______.
Form one linkage group
Will not from any linkage groups
Form interactive groups that affect the phenotype
Form different groups depending upon their relative distance
Conditions of a karyotype 2n ± 1 and 2n ± 2 are called ______.
Aneuploidy
Polyploidy
Allopolyploidy
Monosomy
Distance between the genes and percentage of recombination shows ______.
a direct relationship
an inverse relationship
a parallel relationship
no relationship
If a genetic disease is transferred from a phenotypically normal but carrier female to only some of the male progeny, the disease is ______.
Sex-linked recessive
Autosomal dominant
Sex-linked dominant
Autosomal recessive
In sickle cell anaemia glutamic acid is replaced by valine. Which one of the following triplets codes for valine?
G U G
G A A
A A G
G G G
Person having genotype IA IB would show the blood group as AB. This is because of ______.
Co-dominance
Pleiotropy
Segregation
Incomplete dominance
ZZ / ZW type of sex determination is seen in ______.
Peacock
Cockroach
Platypus
Snails
A cross between two tall plants resulted in offspring having few dwarf plants. What would be the genotypes of both the parents?
Tt and Tt
TT and Tt
TT and TT
Tt and tt
In a dihybrid cross, if you get 9:3:3:1 ratio it denotes that ______.
The allels of two genes are segregating independently
It is a case of multiple allelism
It is a multigenic inheritance
The allels of two genes are interacting with each other
Which of the following will not result in variations among siblings?
Linkage
Mutation
Independent assortment of genes
Crossing over
Mendel’s Law of independent assortment holds good for genes situated on the ______.
non-homologous chromosomes
homologous chromosomes
extranuclear genetic element
same chromosome
Occasionally, a single gene may express more than one effect. The phenomenon is called ______.
pleiotropy
mosaicism
polygeny
multiple allelism
In a certain taxon of insects some have 17 chromosomes and the others have 18 chromosomes. The 17 and 18 chromosome-bearing organisms are ______.
males and females, respectively
females and males, respectively
all males
all females
The inheritance pattern of a gene over generations among humans is studied by the pedigree analysis. Character studied in the pedigree analysis is equivalent to ______.
Mendelian trait
polygenic trait
maternal trait
quantitative trait
It is said that Mendel proposed that the factor controlling any character is discrete and independent. This proposition was based on the ______.
observations that the offspring of a cross made between the plants having two contrasting characters shows only one character without any blending
self pollination of F1 offsprings
cross pollination of parental generations
All of these
Two genes ‘A’ and ‘B’ are linked. In a dihybrid cross involving these two genes, the F1 heterozygote is crossed with homozygous recessive parental type (aa bb). What would be the ratio of offspring in the next generation?
1 : 1 : 1: 1
9 : 3 : 3 : 1
3 : 1
1 : 1
In the F2 generation of a Mendelian dihybrid cross the number of phenotypes and genotypes are ______.
phenotypes - 4; genotypes - 16
phenotypes - 9; genotypes - 4
phenotypes - 4; genotypes - 8
phenotypes - 4; genotypes - 9
Mother and father of a person with ‘O’ blood group have ‘A’ and ‘B’ blood group respectively. What would be the genotype of both mother and father?
Both mother and father are heterozygous for ‘A’ and ‘B’ blood group, respectively
Both mother and father are homozygous for ‘A’ and ‘B’ blood group, respectively
Mother is heterozygous for ‘A’ blood group and father is homozygous for ‘B
Mother is homozygous for ‘A’ blood group and father is heterozygous for ‘B’
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 12 5 Principle of Inheritance and Variation VERY SHORT ANSWER [Pages 32 - 33]
What is the cross between the progeny of F1 and the homozygous recessive parent called? How is it useful?
Do you think Mendel’s laws of inheritance would have been different if the characters that he chose were located on the same chromosome.
Enlist the steps of controlled cross pollination. Would emasculation be needed in a cucurbit plant? Give reasons for your answer.
A person has to perform crosses for the purpose of studying inheritance of a few traits/characters. What should be the criteria for selecting the organisms?
The pedigree chart given below shows a particular trait which is absent in parents but present in the next generatoin irrespective of sexes. Draw your conclusion on the basis of the pedigree.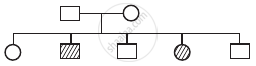
In order to obtain the F1 generation Mendel pollinated a pure-breeding tall plant with a pure breeding dwarf plant. But for getting the F2 generation, he simply self-pollinated the tall F1 plants. Why?
“Genes contain the information that is required to express a particular trait.” Explain.
How are alleles of particular gene differ from each other? Explain its significance.
In a monohybrid cross of plants with red and white flowered plants, Mendel got only red-flowered plants. On self-pollinating these F1 plants got both red and white flowered plants in 3:1 ratio. Explain the basis of using RR and rr symbols to represent the genotype of plants of parental generation.
For the expression of traits genes provide only the potentiality and the environment provides the opportunity. Comment on the veracity of the statement.
A, B, D are three independently assorting genes with their recessive alleles a, b, d respectively. A cross was made between individuals of Aa bb DD genotype with aa bb dd. Explain the type of genotypes of the offspring produced.
In our society a woman is often blamed for not bearing male child. Do you think it is right? Justify.
Discuss the genetic basis of wrinkled phenotype of pea seed.
Even if a character shows multiple allelism, an individual will only have two alleles for that character. Why?
How does a mutagen induce mutation? Explain with example.
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 12 5 Principle of Inheritance and Variation SHORT ANSWER [Pages 33 - 34]
In a Mendelian monohybrid cross, the F2 generation shows identical genotypic and phenotypic ratios. What does it tell us about the nature of alleles involved? Justify your answer.
Can a child have blood group O if his parents have blood group ‘A’ and ‘B’. Explain.
What is Down’s syndrome? Give its symptoms and cause. Why is it that the chances of having a child with Down’s syndrome increases if the age of the mother exceeds forty years?
How was it concluded that genes are located on chromosomes?
A plant with red flowers was crossed with another plant with yellow flowers. If F1 showed all flowers orange in colour, explain the inheritance.
What are the characteristic features of a true-breeding line?
In peas, tallness is dominant over dwarfness, and red colour of flowers is dominant over the white colour. When a tall plant bearing red flowers was pollinated with a dwarf plant bearing white flowers, the different phenotypic groups were obtained in the progeny in numbers mentioned against them:
Tall, Red = 138
Tall, White = 132
Dwarf, Red = 136
Dwarf, White = 128
Mention the genotypes of the two parents and of the four offspring types.
Why is the frequency of red-green colour blindness is many times higher in males than that in females?
If a father and son are both defective in red-green colour vision, is it likely that the son inherited the trait from his father? Comment.
Discuss why Drosophila has been used extensively for genetical studies.
How do genes and chromosomes share similarity from the point of view of genetical studies?
What is recombination? Discuss the applications of recombination from the point of view of genetic engineering.
What is artificial selection? Do you think it affects the process of natural selection? How?
With the help of an example differentiate between incomplete dominance and co-dominance.
It is said, that the harmful alleles get eliminated from population over a period of time, yet sickle cell anaemia is persisting in human population. Why?
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 12 5 Principle of Inheritance and Variation LONG ANSWER [Page 35]
In a plant tallness is dominant over dwarfness and red flower is dominant over white. Starting with the parents work out a dihybrid cross. What is standard dihybrid ratio? Do you think the values would deviate if the two genes in question are interacting with each other?
In humans, males are heterogametic and females are homogametic. Explain. Are there any examples where males are homogametic and females heterogametic?
Also describe as to, who determines the sex of an unborn child? Mention whether temperature has a role in sex determination.
A normal visioned woman, whose father is colour blind, marries a normal visioned man. What would be probability of her sons and daughters to be colour blind? Explain with the help of a pedigree chart.
Discuss in detail the contributions of Morgan and Sturvant in the area of genetics.
Define aneuploidy. How is it different from polyploidy? Describe the individuals having following chromosomal abnormalities.
- Trisomy of 21st Chromosome
- XXY
- XO
Solutions for 5: Principle of Inheritance and Variation
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 12 chapter 5 - Principle of Inheritance and Variation NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 12 chapter 5 - Principle of Inheritance and Variation - Shaalaa.com](/images/biology-english-class-12_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 12 chapter 5 - Principle of Inheritance and Variation
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Biology [English] Class 12 CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics Biology [English] Class 12 CBSE 5 (Principle of Inheritance and Variation) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT Exemplar textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Biology [English] Class 12 chapter 5 Principle of Inheritance and Variation are Mendelian Inheritance - Mendel’s Law of Heredity, Extensions of Mendelian Genetics (Deviation from Mendelism), Polygenic Inheritance, Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance, Genetic Disorders, Linkage and Crossing Over, Sex Determination in Birds, The Law of Dominance, The Law of Segregation (Law of Purity of Gametes), Intragenic Interactions - Incomplete Dominance, Intragenic Interactions - Codominance, Gregor Johann Mendel – Father of Genetics, Introduction of Principles of Inheritance and Variation, Principles of Inheritance and Variation Question, Monohybrid Cross, Sex Determination in Honey Bees, Concept of Mutation, Pedigree Analysis, Mendelian Genetics, Mendelism, Terminology Related to Mendelism, Mendel’s experiments on pea plant, Punnett Square, The Law of Independent Assortment, Intragenic Interactions - Incomplete Dominance, Intragenic Interactions - Dominance, Intragenic Interactions - Codominance, Chromosomal Abnormalities, Heredity and Variation, Multiple Alleles, Intragenic Interactions - Pleiotropy, Comparison Between Gene and Chromosome Behaviour, Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance: Law of Segregation, Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance: Law of Independent Assortment, Linkage and Recombination, Sex Determination, Sex Determination in Some Insects, Sex Determination in Human, Back Cross and Test Cross, Historical Development of Chromosome Theory, Gregor Johann Mendel – Father of Genetics.
Using NCERT Exemplar Biology [English] Class 12 solutions Principle of Inheritance and Variation exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Exemplar Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Biology [English] Class 12 students prefer NCERT Exemplar Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 5, Principle of Inheritance and Variation Biology [English] Class 12 additional questions for Mathematics Biology [English] Class 12 CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
