Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
If a genetic disease is transferred from a phenotypically normal but carrier female to only some of the male progeny, the disease is ______.
Options
Sex-linked recessive
Autosomal dominant
Sex-linked dominant
Autosomal recessive
Solution
If a genetic disease is transferred from a phenotypically normal but carrier female to only some of the male progeny, the disease is sex-linked recessive.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Given below is the representation of amino acid composition not the relevant translated portion of β-chain of haemoglobin, related to the shape of human red blood cells
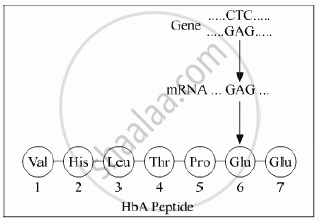
(a) Is this representation indicating a normal human or a sufferer from certain related genetic disease? Give reason in support of your answer.
(b) What difference would be noticed in the phenotype of the normal and the sufferer related to this gene?
(c) Who are likely to suffer more from the defect related to the gene represented the males, the females or both males and females equally? And why?
Why is pedigree analysis done in the study of human genetics? State the conclusions that can be drawn from it.
In sickle cell anaemia glutamic acid is replaced by valine. Which one of the following triplets codes for valine?
It is well known that Queen Victoria of England was a carrier for haemophilia. Since this is an X-linked disease, it can be predicted that ______.
Mental retardation in man associated with sex chromosomal abnormality is usually due to ______.
Trisomy is represented by ______.
Read the following and answer from given below:
According to Mendel, one gene controls the expression of one character only. The ability of a gene to have multiple phenotypic effects because it influences a number of characters are an exception. The gene has multiple phenotypic effects because its ability to control two or more characters can be seen in cotton. In cotton, a gene for the lint also influences the height of the plant, size of the ball, number of ovules, and viability of seeds.
Which of the following disorder is an example of genes with multiple phenotypic effects?
Why is the frequency of red-green colour blindness is many times higher in males than that in females?
Mention any one symptom of Turner's syndrome.
Describe Klinefelter’s syndrome.
