Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Is Matter Around Us Pure
3: Atoms and Molecules
4: Structure of the Atom
5: The Fundamental Unit of Life
6: Tissues
7: Diversity In Living Organisms
8: Motion
9: Force and Laws of Motion
10: Gravitation
▶ 11: Work and Energy
12: Sound
13: Why Do We Fall Ill
14: Natural Resources
15: Improvement In Food Resources
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Science [English] Class 9 chapter 11 - Work and Energy NCERT Exemplar solutions for Science [English] Class 9 chapter 11 - Work and Energy - Shaalaa.com](/images/science-english-class-9_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 11: Work and Energy
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 11 of CBSE NCERT Exemplar for Science [English] Class 9.
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Science [English] Class 9 11 Work and Energy Multiple Choice Questions [Pages 68 - 69]
When a body falls freely towards the earth, then its total energy
increases
decreases
remains constant
first increases and then decreases
A car is accelerated on a levelled road and attains a velocity 4 times of its initial velocity. In this process the potential energy of the car
does not change
becomes twice to that of initial
becomes 4 times that of initial
becomes 16 times that of initial
In the case of negative work, the angle between the force and displacement is
0°
45°
90°
180°
An iron sphere of mass 10 kg has the same diameter as an aluminium sphere of mass 3.5 kg. Both the spheres are dropped simultaneously from a tower. When they are 10 m above the ground, they have the same :
acceleration
momentum
potential energy
kinetic energy
A girl is carrying a school bag of 3 kg mass on her back and moves 200 m on a levelled road. The work done against the gravitational force will be (g = 10 m s–2)
6 ×103 J
6 J
0.6 J
zero
Which one of the following is not the unit of energy?
joule
newton metre
kilowatt
kilowatt-hour
The work done on an object does not depend upon the
displacement
force applied
the angle between force and displacement
the initial velocity of the object
Water stored in a dam possesses :
no energy
electrical energy
kinetic energy
potential energy
A body is falling from a height of h. After it has fallen a height `"h"/2`, it will possess
only potential energy
only kinetic energy
half potential and half kinetic energy
more kinetic and less potential energy
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Science [English] Class 9 11 Work and Energy Short Answer Questions [Pages 69 - 70]
A rocket is moving up with a velocity v. If the velocity of this rocket is suddenly tripled, what will be the ratio of two kinetic energies?
Avinash can run with a speed of 8 m s–1 against the frictional force of 10 N, and Kapil can move with a speed of 3 m s–1 against the frictional force of 25 N. Who is more powerful and why?
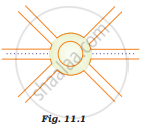
A boy is moving on a straight road against a frictional force of 5 N. After travelling a distance of 1.5 km he forgot the correct path at a roundabout (Fig. 11.1) of radius 100 m. However, he moves on the circular path for one and half-cycle and then he moves forward up to 2.0 km. Calculate the work done by him.
Can any object have mechanical energy even if its momentum is zero? Explain.
Can any object have momentum even if its mechanical energy is zero? Explain
The power of a motor pump is 2 kW. How much water per. the minute the pump can raise to a height of 10 m? (Given g = 10m s−2)
The weight of a person on planet A is about half that on the earth. He can jump up to 0.4 m in height on the surface of the earth. How high he can jump on planet A?
The velocity of a body moving in a straight line is increased by applying a constant force F, for some distance in the direction of the motion. Prove that the increase in the kinetic energy of the body is equal to the work done by the force on the body.
Is it possible that an object is in a state of accelerated motion due to external force acting on it, but no work is being done by the force? Explain it with an example.
A ball is dropped from a height of 10 m. If the energy of the ball reduces by 40% after striking the ground, how much high can the ball bounce back? (g = 10 m s–2)
If an electric iron of 1200 W is used for 30 minutes every day, find electric energy consumed in the month of April.
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Science [English] Class 9 11 Work and Energy Long Answer Questions [Page 70]
A light and a heavy object have the same momentum. Find out the ratio of their kinetic energies. Which one has larger kinetic energy?
An automobile engine propels a 1000 kg car (A) along a levelled road at a speed of 36 km h–1. Find the power if the opposing frictional force is 100 N. Now, suppose after travelling a distance of 200 m, this car collides with another stationary car (B) of the same mass and comes to rest. Let its engine also stop at the same time. Now the car (B) starts moving on the same level road without getting its engine started. Find the speed of the car (B) just after the collision.
A girl with having a mass of 35 kg sits on a trolley of mass 5 kg. The trolley is given an initial velocity of 4 m s–1 by applying a force. The trolley comes to rest after traversing a distance of 16 m. (a) How much work is done on the trolley? (b) How much work is done by the girl?
Four men lift a 250 kg box to a height of 1 m and hold it without raising or lowering it.
(a) How much work is done by the men in lifting the box?
(b) How much work do they do in just holding it?
(c) Why do they get tired while holding it? (g = 10 m s–2)
What is power? How do you differentiate kilowatt from kilowatt-hour? The Jog Falls in Karnataka state are nearly 20 m high. 2000 tonnes of waterfalls from it in a minute. Calculate the equivalent power if all this energy can be utilized? (g = 10 m s–2)
How is the power related to the speed at which a body can be lifted? How many kilograms will a man working at the power of 100 W, be able to lift at a constant speed of 1 m s–1 vertically? (g = 10 m s–2)
Define watt. Express kilowatt in terms of joule per second. A 150 kg car engine develops 500 W for each kg. What force does it exert in moving the car at a speed of 20 ms–1?
Compare the power at which each of the following is moving upwards against the force of gravity? (given g = 10 m s–2)
a butterfly of mass 1.0 g that flies upward at a rate of 0.5 ms–1.
Compare the power at which each of the following is moving upwards against the force of gravity? (given g = 10 m s–2)
a 250 g squirrel climbing up on a tree at a rate of 0.5 ms–1.
Solutions for 11: Work and Energy
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Science [English] Class 9 chapter 11 - Work and Energy NCERT Exemplar solutions for Science [English] Class 9 chapter 11 - Work and Energy - Shaalaa.com](/images/science-english-class-9_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Science [English] Class 9 chapter 11 - Work and Energy
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Science [English] Class 9 CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics Science [English] Class 9 CBSE 11 (Work and Energy) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT Exemplar textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Science [English] Class 9 chapter 11 Work and Energy are Concept of Work, Energy, Concept of Work, Potential Energy of an Object at a Height, Mechanical Energy, Kinetic Energy (K), Potential Energy (U), Gravitational Potential Energy, Transformation of Energy, Law of Conservation of Energy, Rate of Doing Work, Work and Energy (Numericals).
Using NCERT Exemplar Science [English] Class 9 solutions Work and Energy exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Exemplar Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Science [English] Class 9 students prefer NCERT Exemplar Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 11, Work and Energy Science [English] Class 9 additional questions for Mathematics Science [English] Class 9 CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
