Advertisements
Chapters
![NCERT solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 6 chapter 3 - Playing with Numbers NCERT solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 6 chapter 3 - Playing with Numbers - Shaalaa.com](/images/mathematics-english-class-6_6:0797baf62bd6489d8c888098e76ae949.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 3: Playing with Numbers
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 3 of CBSE NCERT for Mathematics [English] Class 6.
NCERT solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 6 3 Playing with Numbers Exercise 3.1 [Pages 50 - 51]
Write all the factors of the following number.
24
Write all the factors of the following number.
15
Write all the factors of the following number.
21
Write all the factors of the following number.
27
Write all the factors of the following number.
12
Write all the factors of the following number.
20
Write all the factors of the following number.
18
Write all the factors of the following number.
23
Write all the factors of the following number.
36
Write first five multiples of 5.
Write first five multiple of 8.
Write first five multiples of 9.
Match the items in column 1 with the items in column 2.
|
|
Column 1 |
|
Column 2 |
|
(i) |
35 |
(a) |
Multiple of 8 |
|
(ii) |
15 |
(b) |
Multiple of 7 |
|
(iii) |
16 |
(c) |
Multiple of 70 |
|
(iv) |
20 |
(d) |
Factor of 30 |
|
(v) |
25 |
(e) |
Factor of 50 |
|
|
|
(f) |
Factor of 20 |
Find all the multiples of 9 up to 100.
NCERT solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 6 3 Playing with Numbers Exercise 3.2 [Pages 53 - 54]
What is the sum of any two Odd numbers?
Odd
Even
What is the sum of any two Even numbers?
Odd
Even
State whether the following statement is True or False:
The sum of three odd numbers is even.
True
False
The sum of two odd numbers and one even number is even.
True
False
The product of three odd numbers is odd.
True
False
If an even number is divided by 2, the quotient is always odd.
True
False
All prime numbers are odd.
True
False
Prime numbers do not have any factors.
True
False
The Sum of two prime numbers is always even.
True
False
2 is the only even prime number.
True
False
All even numbers are composite numbers.
True
False
The product of two even numbers is always even.
True
False
The numbers 13 and 31 are prime numbers. Both these numbers have the same digits 1 and 3. Find such pairs of prime numbers up to 100.
Write down separately the prime and composite numbers less than 20.
What is the greatest prime number between 1 and 10?
Express the following as the sum of two odd primes.
44
Express the following number as the sum of two odd prime:
36
Express the following as the sum of two odd prime.
24
Express the following as the sum of two odd prime.
18
Give three pairs of prime numbers whose difference is 2.
[Remark: Two prime numbers whose difference is 2 are called twin primes].
Which of the following number is prime?
23
Which of the following number is prime?
51
Which of the following number is prime?
37
Which of the following number is prime?
26
Write seven consecutive composite numbers less than 100 having no prime number between them.
Express the following number as the sum of three odd primes:
21
Express the following number as the sum of three odd primes:
31
Express the following number as the sum of three odd primes:
53
Express the following number as the sum of three odd primes:
61
Write five pairs of prime numbers less than 20 whose sum is divisible by 5. (Hint : 3 + 7 = 10)
Fill in the blanks:
A number which has only two factors is called a ______.
A number which has more than two factors is called a ______.
1 is neither ______ nor ______.
The smallest prime number is ______.
The smallest composite number is ______.
The smallest even number is ______.
NCERT solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 6 3 Playing with Numbers Exercise 3.3 [Pages 57 - 58]
Using divisibility tests, determine which of the following numbers are divisible by 2; by 3; by 4; by 5; by 6; by 8; by 9; by 10; by 11 (say, yes or no):
|
Number |
Divisible by |
||||||||
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
|
|
128 |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
No |
No |
Yes |
No |
No |
No |
|
990 |
______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ |
|
1586 |
______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ |
|
275 |
______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ |
|
6686 |
______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ |
|
639210 |
______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ |
|
429714 |
______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ |
|
2856 |
______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ |
|
3060 |
______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ |
|
406839 |
______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ |
Using the divisibility test, determine which of the following number is divisible by 4; by 8:
572
Using the divisibility test, determine which of the following number is divisible by 4; by 8:
726352
Using the divisibility test, determine which of the following number is divisible by 4; by 8:
5500
Using the divisibility test, determine which of the following number is divisible by 4; by 8:
6000
Using the divisibility test, determine which of the following number is divisible by 4; by 8:
12159
Using the divisibility test, determine which of the following number is divisible by 4; by 8:
14560
Using the divisibility test, determine which of the following number is divisible by 4; by 8:
21084
Using the divisibility test, determine which of the following number is divisible by 4; by 8:
31795072
Using the divisibility test, determine which of the following number is divisible by 4; by 8:
1700
Using the divisibility test, determine which of the following number is divisible by 4; by 8:
2150
Using the divisibility test, determine which of the following number is divisible by 6:
297144
Using the divisibility test, determine which of the following number is divisible by 6:
1258
Using the divisibility test, determine which of the following number is divisible by 6:
4335
Using the divisibility test, determine which of the following number is divisible by 6:
61233
Using the divisibility test, determine which of the following number is divisible by 6:
901352
Using the divisibility test, determine which of the following number is divisible by 6:
438750
Using the divisibility test, determine which of the following number is divisible by 6:
1790184
Using the divisibility test, determine which of the following number is divisible by 6:
12583
Using the divisibility test, determine which of the following number is divisible by 6:
639210
Using the divisibility test, determine which of the following number is divisible by 6:
17852
Using the divisibility test, determine which of the following number is divisible by 11:
5445
Using the divisibility test, determine which of the following number is divisible by 11:
10824
Using the divisibility test, determine which of the following number is divisible by 11:
7138965
Using the divisibility test, determine which of the following number is divisible by 11:
70169308
Using the divisibility test, determine which of the following number is divisible by 11:
10000001
Using the divisibility test, determine which of the following number is divisible by 11:
901153
Write the smallest digit and the greatest digit in the blank space of the following number so that the number formed is divisible by 3:
______ 6724
Write the smallest digit and the greatest digit in the blank space of the following number so that the number formed is divisible by 3:
4765 ______ 2
Write a digit in the blank space of the following number so that the number formed is divisible by 11:
92 ______ 389
Write a digit in the blank space of the following number so that the number formed is divisible by 11:
8 ______ 9484
NCERT solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 6 3 Playing with Numbers Exercise 3.4 [Page 59]
Find the common factor of:
20 and 28
Find the common factor of:
15 and 25
Find the common factor of:
35 and 50
Find the common factor of:
56 and 120
Find the common factors of:
4, 8 and 12
Find the common factors of:
5, 15, and 25.
Find the first three common multiples of:
6 and 8
Find the first three common multiples of:
12 and 18
Write all the numbers less than 100 which are common multiples of 3 and 4.
Which of the following numbers is co-prime?
18 and 35
Which of the following numbers is co-prime?
15 and 37
Which of the following numbers is co-prime?
30 and 415
Which of the following numbers is co-prime?
17 and 68
Which of the following numbers is co-prime?
216 and 215
Which of the following numbers is co-prime?
81 and 16
A number is divisible by both 5 and 12. By which other numbers will that number be always divisible?
A number is divisible by 12. By what other numbers will that number be divisible?
NCERT solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 6 3 Playing with Numbers Exercise 3.5 [Pages 61 - 62]
Which of the following statement is true?
If a number is divisible by 3, it must be divisible by 9.
True
False
Which of the following statement is true?
If a number is divisible by 9, it must be divisible by 3.
True
False
Write (T) for true and (F) for false against the following statement:
A number is divisible by 18 if it is divisible by both 3 and 6.
True
False
Write (T) for true and (F) for false against the following statement:
If a number is divisible by both 9 and 10, it must be divisible by 90.
True
False
State the following statement as True or False.
If two numbers are co-primes, at least one of them must be a prime number.
True
False
Which of the following statement is true?
All numbers which are divisible by 4 must also be divisible by 8.
True
False
Which of the following statement is true?
All numbers which are divisible by 8 must also be divisible by 4.
True
False
Which of the following statement is true?
If a number exactly divides two numbers separately, it must exactly divide their sum.
True
False
Write (T) for true and (F) for false against the following statement:
If a number divides the sum of two numbers exactly, it must exactly divide the numbers separately.
True
False
Here are the different factor trees for 60. Write the missing numbers.
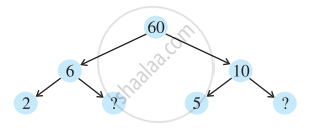
Here are the different factor trees for 60. Write the missing numbers.
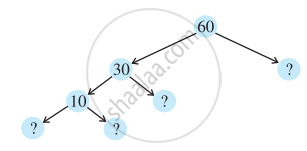
Which factors are not included in the prime factorisation of a composite number?
Write the greatest 4-digit number and express it in terms of its prime factors.
Write the smallest 5-digit number and express it in the form of its prime factors.
Find all the prime factors of 1729 and arrange them in ascending order. Now state the relation, if any; between two consecutive prime factors.
The product of any three consecutive numbers is always divisible by 6. Justify this statement with an example
The sum of two consecutive odd numbers is divisible by 4. Verify this statement with the help of some examples.
In which of the following expressions, prime factorization has been done?
24 = 2 × 3 × 4
In which of the following expressions, prime factorization has been done?
56 = 7 × 2 × 2 × 2
In which of the following expressions, prime factorisation has been done?
70 = 2 × 5 × 7
In which of the following expressions, prime factorization has been done?
54 = 2 × 3 × 9
Determine if 25110 is divisible by 45.
[Hint: 5 and 9 are co-prime numbers. Test the divisibility of the numbers 5 and 9].
18 is divisible by both 2 and 3. It is also divisible by 2 × 3 = 6. Similarly, a number is divisible by both 4 and 6. Can we say that the number must also be divisible by 4 × 6 = 24? If not, give an example to justify your answer.
I am the smallest number, having four different prime factors. Can you find me?
NCERT solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 6 3 Playing with Numbers Exercise 3.6 [Pages 63 - 64]
Find the HCF of the following numbers:
18, 48
Find the HCF of the following numbers:
30, 42
Find the HCF of the following numbers:
18, 60
Find the HCF of the following numbers:
27, 63
Find the HCF of the following numbers:
36, 84
Find the HCF of the following numbers:
34, 102
Find the HCF of the following numbers:
70, 105, 175
Find the HCF of the following numbers:
91, 112, 49.
Find the HCF of the following numbers:
18, 54, 81
Find the HCF of the following numbers:
12, 45, 75
What is the HCF of two consecutive numbers?
What is the HCF of two consecutive even numbers?
What is the HCF of two consecutive odd numbers?
HCF of co-prime numbers 4 and 15 was found as follows by factorization:
4 = 2 × 2 and 15 = 3 × 5 since there is no common prime factor, so HCF of 4 and 15 is 0. Is the answer correct? If not, what is the correct HCF?
NCERT solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 6 3 Playing with Numbers Exercise 3.7 [Page 67]
Renu purchases two bags of fertilizer of weights 75 kg and 69 kg. Find the maximum value of weight which can measure the weight of the fertilizer the exact number of times.
Three boys step off together from the same spot. Their steps measure 63 cm, 70 cm, and 77 cm respectively. What is the minimum distance each should cover so that all can cover the distance in complete steps?
The length, breadth, and height of a room are 825 cm, 675 cm, and 450 cm respectively. Find the longest tape which can measure the three dimensions of the room exactly.
Determine the smallest 3-digit number which is exactly divisible by 6, 8, and 12.
Determine the greatest 3-digit number exactly divisible by 8, 10 and 12.
The traffic lights at three different road crossings change after every 48 seconds, 72 seconds, and 108 seconds respectively. If they change simultaneously at 7 a.m., at what time will they change simultaneously again?
Three tankers contain 403 litres, 434 litres and 465 litres of diesel respectively. Find the maximum capacity of a container that can measure the diesel of the three containers an exact number of times.
Find the least number which when divided by 6, 15 and 18 leave the remainder of 5 in each case.
Find the smallest 4-digit number which is divisible by 18, 24 and 32.
Find the LCM of the following numbers:
- 9 and 4
- 12 and 5
- 6 and 5
- 15 and 4
Observe a common property in the obtained LCMs. Is LCM the product of two numbers in each case?
Find the LCM of the following numbers in which one number is the factor of the other.
- 5, 20
- 6, 18
- 12, 48
- 9, 45
What do you observe in the results obtained?
Solutions for 3: Playing with Numbers
![NCERT solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 6 chapter 3 - Playing with Numbers NCERT solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 6 chapter 3 - Playing with Numbers - Shaalaa.com](/images/mathematics-english-class-6_6:0797baf62bd6489d8c888098e76ae949.jpg)
NCERT solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 6 chapter 3 - Playing with Numbers
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 6 CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT solutions for Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 6 CBSE 3 (Playing with Numbers) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Mathematics [English] Class 6 chapter 3 Playing with Numbers are Arranging the Objects in Rows and Columns, Factors and Multiples, Concept of Perfect Number, Concept of Prime Numbers, Concept of Co-Prime Number, Concept of Twin Prime Numbers, Concept of Even and Odd Number, Concept of Composite Number, Eratosthenes’ method of finding prime numbers, Tests for Divisibility of Numbers, Divisibility by 10, Divisibility by 5, Divisibility by 2, Divisibility by 3, Divisibility by 6, Divisibility by 4, Divisibility by 8, Divisibility by 9, Divisibility by 11, Common Factor, Common Multiples, Some More Divisibility Rules, Prime Factorisation, Highest Common Factor, Lowest Common Multiple, Arranging the Objects in Rows and Columns, Factors and Multiples, Concept of Perfect Number, Concept of Prime Numbers, Concept of Co-Prime Number, Concept of Twin Prime Numbers, Concept of Even and Odd Number, Concept of Composite Number, Eratosthenes’ method of finding prime numbers, Tests for Divisibility of Numbers, Divisibility by 10, Divisibility by 5, Divisibility by 2, Divisibility by 3, Divisibility by 6, Divisibility by 4, Divisibility by 8, Divisibility by 9, Divisibility by 11, Common Factor, Common Multiples, Some More Divisibility Rules, Prime Factorisation, Highest Common Factor, Lowest Common Multiple.
Using NCERT Mathematics [English] Class 6 solutions Playing with Numbers exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Mathematics [English] Class 6 students prefer NCERT Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 3, Playing with Numbers Mathematics [English] Class 6 additional questions for Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 6 CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
