Topics
Introduction of Sociology
Contribution of Western and Indian Sociologists
- Introduction to Western Sociologists
- Auguste Comte (1798-1857)
- Emile Durkheim (1858-1917)
- Karl Marx (1818-1883)
- Abdul Rahman Ibn-khaldun
- Harriet Martineau (1802 – 1876)
- Durkheims’ Theory of Suicide
- William Du Bois (1868 – 1963)
- Marxian Theory of ‘Class Conflict’
- Introduction to Indian Sociologists
- Dr. G. S. Ghurye (1893-1983)
- Dr. M. N. Srinivas (1916-1999)
- Dr. Iravati Karve (1905-1970)
Basic Concepts in Sociology
- Introduction of Society
- Definition of Society
- Characteristics of Society
- Introduction of Community
- Definition of Community
- Elements of Community
- Introduction of Social Group
- Definition of Social Group
- Characteristics of Social Group
- Types of Social Group
- Concept of Social Status
- Types of Social Status
- Concept of Social Role
- Social Role Related Concept
- Concept of Social Norms
- Types of Social Norms
Social Institutions
- Concept of Social Institutions
- Characteristics of Social Institutions
- Concept of Family
- Functions of Family
- Forms of Family
- Twenty-first Century Families
- Concept of Marriage
- Forms of Marriage
- Family, Marriage and Kinship
- Economy and Work
- Concept of Education
- Types of Education
- Importance of Education
- Education and Social Division
Culture
Socialization
Social Stratification
Social Change
Notes
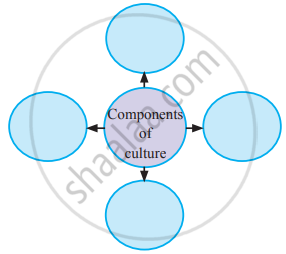
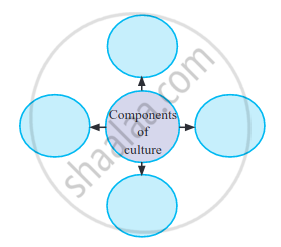
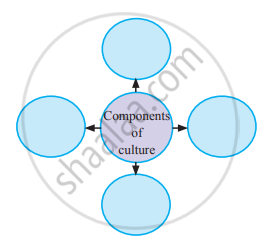
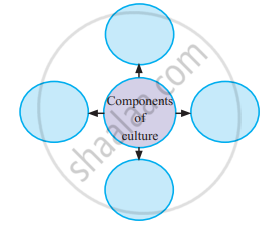
Components of Culture:
1. Symbols: Every culture is filled with symbols, or things that stand for something else and that often evoke various reactions and emotions. The first element that exists in every culture is a variety of symbols. For example, with the extensive use of mobile, emojis/ emoticons are widely used to express and communicate various emotions.Emojis/smileys are combinations of keyboard characters that many use to represent their feelings online or through texting. Similarly, the Indian flag represents our entire country.
2. Language: A group of words or ideas having common meaning and is shared in a social situation is called language. Language is a set of socially sound patterns, words, and sentences having specific meaning and terminology common to the same culture. Language is like a vehicle through which we can carry out our complex social activities. Language is the foundation of culture.
3. Knowledge: Knowledge is one of the most important elements of culture. With the help of knowledge, an individual knows how to cope with the existing social situation. Knowledge could be direct or indirect. Direct knowledge is immediate knowledge, whereas indirect knowledge is mediated knowledge.
4. Values and Beliefs: Values are another important element of culture and involve standards of what is good or bad, and desirable or undesirable. Both cultural values and beliefs form the core of our moral world-view.
5. Norms: Norms are rules and behavioural expectations by which a society guides the behaviours of its members. Social norms are further divided into folkways and mores. Folkways are mildly enforced social expectations, while mores are strictly held beliefs about behaviours. Mores are more compulsory to follow than are folkways.