Topics
Units and Measurements
- Introduction of Units and Measurements
- System of Units
- Measurement of Length
- Measurement of Mass
- Measurement of Time
- Dimensions and Dimensional Analysis
- Accuracy, Precision and Uncertainty in Measurement
- Errors in Measurements
- Significant Figures
Mathematical Methods
- Vector Analysis
- Vector Operations
- Resolution of Vectors
- Multiplication of Vectors
- Introduction to Calculus
Motion in a Plane
- Introduction to Motion in a Plane
- Rectilinear Motion
- Motion in Two Dimensions-Motion in a Plane
- Uniform Circular Motion (UCM)
Laws of Motion
- Introduction to Laws of Motion
- Aristotle’s Fallacy
- Newton’s Laws of Motion
- Inertial and Non-inertial Frames of Reference
- Types of Forces
- Work Energy Theorem
- Principle of Conservation of Linear Momentum
- Collisions
- Impulse of Force
- Rotational Analogue of a Force - Moment of a Force Or Torque
- Couple and Its Torque
- Mechanical Equilibrium
- Centre of Mass
- Centre of Gravity
Gravitation
- Introduction to Gravitation
- Kepler’s Laws
- Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation
- Measurement of the Gravitational Constant (G)
- Acceleration Due to Gravity (Earth’s Gravitational Acceleration)
- Variation in the Acceleration Due to Gravity with Altitude, Depth, Latitude and Shape
- Gravitational Potential and Potential Energy
- Earth Satellites
Mechanical Properties of Solids
- Introduction to Mechanical Properties of Solids
- Elastic Behavior of Solids
- Stress and Strain
- Hooke’s Law
- Elastic Modulus
- Stress-strain Curve
- Strain Energy
- Hardness
- Friction in Solids
Thermal Properties of Matter
- Introduction to Thermal Properties of Matter
- Heat and Temperature
- Measurement of Temperature
- Absolute Temperature and Ideal Gas Equation
- Thermal Expansion
- Specific Heat Capacity
- Calorimetry
- Change of State
- Heat Transfer
- Newton’s Law of Cooling
Sound
- Introduction to Sound
- Types of Waves
- Common Properties of All Waves
- Transverse Waves and Longitudinal Waves
- Mathematical Expression of a Wave
- The Speed of Travelling Waves
- Principle of Superposition of Waves
- Echo, Reverberation and Acoustics
- Qualities of Sound
- Doppler Effect
Optics
- Introduction to Ray Optics
- Nature of Light
- Ray Optics Or Geometrical Optics
- Reflection
- Refraction
- Total Internal Reflection
- Refraction at a Spherical Surface and Lenses
- Dispersion of Light Through Prism and Formation of Spectrum
- Some Natural Phenomena Due to Sunlight
- Defects of Lenses (Aberrations of Optical Images)
- Optical Instruments
- Optical Instruments: Simple Microscope
- Optical Instruments: Compound Microscope
- Optical Instruments: Telescope
Electrostatics
- Introduction to Electrostatics
- Electric Charges
- Basic Properties of Electric Charge
- Coulomb’s Law - Force Between Two Point Charges
- Principle of Superposition
- Electric Field
- Electric Flux
- Gauss’s Law
- Electric Dipole
- Continuous Distribution of Charges
Electric Current Through Conductors
- Electric Current
- Flow of Current Through a Conductor
- Drift Speed
- Ohm's Law (V = IR)
- Limitations of Ohm’s Law
- Electrical Power
- Resistors
- Specific Resistance (Resistivity)
- Variation of Resistance with Temperature
- Electromotive Force (emf)
- Combination of Cells in Series and in Parallel
- Types of Cells
- Combination of Resistors - Series and Parallel
Magnetism
- Introduction to Magnetism
- Magnetic Lines of Force and Magnetic Field
- The Bar Magnet
- Gauss' Law of Magnetism
- The Earth’s Magnetism
Electromagnetic Waves and Communication System
- EM Wave
- Electromagnetic Spectrum
- Propagation of EM Waves
- Introduction to Communication System
- Modulation
Semiconductors
- Introduction to Semiconductors
- Electrical Conduction in Solids
- Band Theory of Solids
- Intrinsic Semiconductor
- Extrinsic Semiconductor
- p-n Junction
- A p-n Junction Diode
- Basics of Semiconductor Devices
- Applications of Semiconductors and P-n Junction Diode
- Thermistor
- Stress
- Types of stress
1) Longitudinal stress: Tensile stress and Compressive stress
2) Hydraulic or volume stress
3) Shear or tangential stress
4) Breaking stress - Strain
- Types of strain
1) Longitudinal (tensile or linear) strain
2) Volume strain
3) Shear strain
Notes
Stress & Strain:
stress:-
The internal restoring force setup per unit area of cross-section of the deformed body is called stress.
If a body gets deformed under the action of an external force, then at each section of the body an internal force of the reaction is set up which tends to restore the body into its original state.
unit:
Its dimensional formula is
Types of stress:
There are different types of stress
1. Longitudinal stress: if deforming force is applied normal to the area of cross-section, then the stress is called longitudinal stress. It is further categorized into two types.
(a) Tensile stress: if there is an increase in the length of the object under the effect of applied force, then stress is called tensile stress.
(b) Compressional stress: If there is a decrease in the length of the object under the effect of applied force, then stress is called compressional stress.

2. Tangential or shearing stress:
If deforming force acts tangentially to the surface of a body, it produces a change in the shape of the body. The tangential force applied per unit area is called tangential stress.
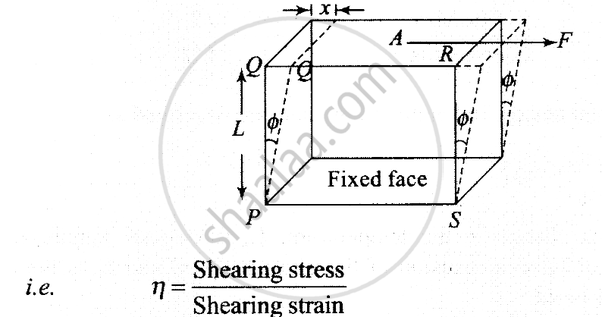
3.Normal stress:
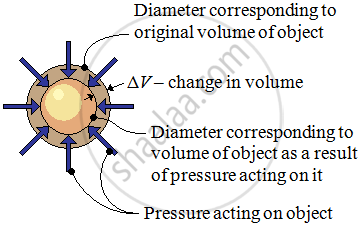
If a body is subjected to a uniform force from all sides, then the corresponding stress is called hydrostatic stress.
Strain:
When a deforming force acts on a body, the body undergoes a change in its shape and size. The fractional change in configuration is called strain.
Strain = change in dimension / original dimension
It has no unit and it is a dimensionless quantity.
Types of strain:
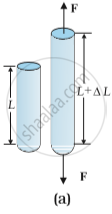
1. Longitudinal strain:
Change in length to the original length of the body due to the longitudinal stress.
-
If we apply longitudinal stress to a body either the body elongates or it compresses this change along the length of the body. This change in length is measured by Longitudinal Strain.
-
Longitudinal Strain =
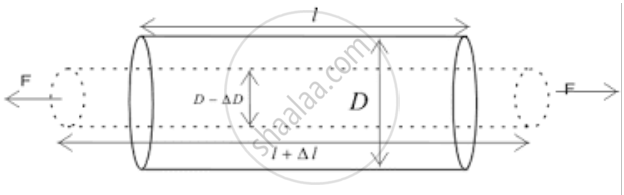
-
Strain occurs as a result of stress.
2. Volumetric strain:
Volume strain is defined as the ratio of change in volume to the original volume as a result of the hydraulic stress.
-
When the stress is applied by a fluid on a body there is a change in the volume of the body without changing the shape of the body.
-
Volume strain =
Therefore, Change in the volume ΔV= V’ – V
-
Conclusion: - Deformation is measured using strain.
-
Consider a cube whose initial volume is V.
-
When the cube is subjected to stress there will be a change in the volume but the shape will not change.

-
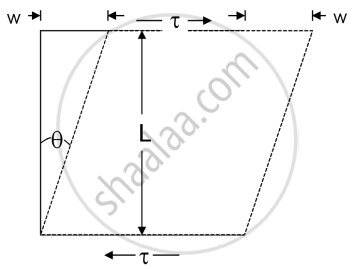
3. Shearing strain =
Shearing strain is the measure of the relative displacement of the opposite faces of the body as a result of shearing stress.
-
If we apply force parallel to the cross-sectional area because of which there was relative displacement between the opposite faces of the body.
-
Shearing strain measures to what extent the two opposite faces got displaced relative to each other.
Shearing strain=
-
In terms of tan θ,
-
Shearing strain = tan θ =
-
tan θ is equal to θ (as θ is very small)
-
Therefore,
-