Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
2 liters of gas is enclosed in a vessel at a pressure of 760 mmHg. If the temperature remains constant, calculate pressure when volume changes to 4 dm3.
उत्तर
V = 2 litres
P = 760 mm
V1 = 4000 m3 [1 dm3 = 4 litres]
P1= ?
`"PV"/"T" = ("P"_1 "V"_1)/"T"_1`
`(760 xx 2)/"T" = ("P"_1 xx 4)/"T"_1`
`"P"_1 = 760/2 = 380` mm
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
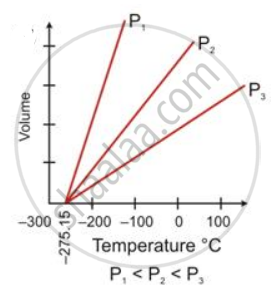
State the law which is represented by the following graph:
State the following:
Ice point in absolute temperature
What will be the minimum pressure required to compress 500 dm3 of air at 1 bar to 200 dm3 temperature remaining constant?
It is found that on heating a gas its volume increases by 50% and its pressure decreases to 60% of its original value. If the original temperature was -15°C, find the temperature to which it was heated.
2500 cm3 of hydrogen is taken at STP. The pressure of this gas is further increased by two and a half times (temperature remaining constant). What volume will hydrogen occupy now?
Correct the following statement:
The volume of a fixed mass of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature, pressure remaining constant.
A certain mass of gas occupied 850 ml at a pressure of 760 mm of Hg. On increasing the pressure it was found that the volume of the gas was 75% of its initial value. Assuming constant temperature, find the final pressure of the gas?
It is required to reduce the volume of a gas by 20% by compressing it at a constant pressure. To do so, the gas has to be cooled. If the gas attains a final temperature of 157°C, find the initial temperature of the gas.
Fill in the blank with the correct word, from the words in option:
If the temperature of a fixed mass of a gas is kept constant and the pressure is increased, the volume correspondingly _______.
The pressure on one mole of gas at s.t.p. is doubled and the temperature is raised to 546 K. What is the final volume of the gas ? [one mole of a gas occupies a volume of 22.4 litres at stp.]
