Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
At constant temperature, the effect of change of pressure on the volume of a gas was as given below:
|
Pressure in atmosphere |
Volume in liters |
|
0.20 |
112 |
|
0.25 |
89.2 |
|
0.40 |
56.25 |
|
0.60 |
37.40 |
|
0.80 |
28.10 |
|
1.00 |
22.4 |
(a) Plot the following graphs
- P vs V
- P vs 1/V
- PV vs P
Interpret each graph in terms of the law.
(b) Assuming that the pressure values given above are correct, find the correct measurement of the volume.
उत्तर
|
P/atm |
V/dm3 |
1/V |
PV |
|
0.2 |
112 |
0.009 |
22.4 |
|
0.25 |
89.2 |
0.011 |
22.4 |
|
0.4 |
56.25 |
0.018 |
22.4 |
|
0.6 |
37.4 |
0.027 |
22.4 |
|
0.8 |
28.1 |
0.036 |
22.4 |
|
1 |
22.4 |
0.045 |
22.4 |
(a) Plot the following graphs:
1. P vs. V:
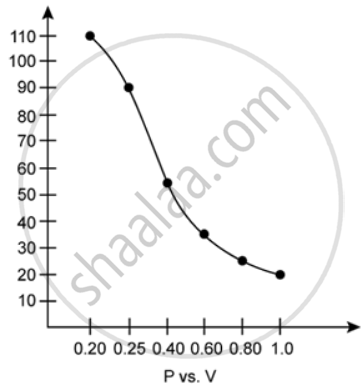
At constant temperature, P is inversely proportional to V. Thus, the plot of V versus P will be a rectangular hyperbola.
2. P vs. 1/V:

According to Boyle's law, at a constant temperature, the pressure of a fixed amount of gas varies inversely to its volume. The graph of pressure versus 1/V shows a positive slope.
3. PV vs. P:

According to Boyle's law, the product of pressure and volume is constant at a constant temperature. The graph of PV versus P is constant which indicates that the given gas obeys Boyle's law.
(b) The correct measurements of the volume are given below:
|
P/atm |
V/dm3 |
|
0.2 |
112 |
|
0.25 |
89.6 |
|
0.4 |
56 |
|
0.6 |
37.33 |
|
0.8 |
28 |
|
1 |
22.4 |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain Boyle's Law on the basis of the kinetic theory of matter.
Give reasons for the following:
It is necessary to specify the pressure and temperature of gas while stating its volume.
Choose the correct answer:
If the pressure is doubled for a fixed mass of a gas, its volume will become
Calculate the volume occupied by 2 g of hydrogen at 27°C and 4-atmosphere pressure if at STP it occupies 22.4 litres.
A given mass of a gas occupied 143 cm3 at 27° C and 700 mm Hg pressure. What will be its volume at 300 K and 280 mm Hg pressure?
Calculate the volume of a gas ‘A’ at s.t.p., if at 37°C and 775 mm of mercury pressure, it occupies a volume of `9 1/2` litres.
Calculate the following:
Calculate the temperature at which a gas ‘A’ at 20°C having a volume, of 500 cc. will occupy a volume of 250 cc.
Calculate the following:
A gas ‘X’ is collected over water at 17°C and 750 mm. pressure. If the volume of the gas collected is 50 cc., calculate the volume of the dry gas at s.t.p. [at 17°C the vapour pressure is 14 mm.]
Assuming temperature remaining constant calculate the pressure of the gas in the following:
The pressure of a gas having volume 1000 cc. originally occupying 1500 cc. at 720 mm. pressure.
Assuming temperature remaining constant calculate the pressure of the gas in the following:
The pressure of a gas having volume 1800 ml. originally occupying 300 ml. at 6 atms. pressure.
