Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Calculate the following:
A gas ‘X’ is collected over water at 17°C and 750 mm. pressure. If the volume of the gas collected is 50 cc., calculate the volume of the dry gas at s.t.p. [at 17°C the vapour pressure is 14 mm.]
उत्तर
Initial conditions
T1 = 17 + 273 = 290 K
P1 = 750 mm - 14 mm
V1 = 50 c.c
Final conditions
T2 = 273 K
P2 = 760 mm
V2 = ?
Using gas equation `("P"_1"V"_1)/"T"_1 = ("P"_2"V"_2)/"T"_2`
∴ V2 = `("P"_1"V"_1"T"_2)/("T"_1"P"_2)`
`= (736 xx 50 xx 273)/(290 xx 760) = 45.58`
⇒ 45.6 cc
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain Why?
Inflating a balloon seems to violate Boyle's law.
State the law which is represented by the following graph:
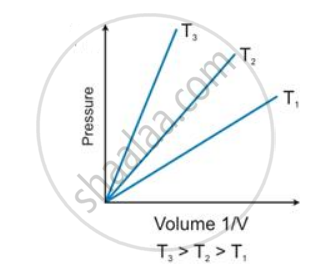
A gas at 240 K is heated to 127°C. Find the percentage change in the volume of the gas (pressure remaining constant).
At 0°C and 760 mmHg pressure, a gas occupies a volume of 100 cm3. Kelvin temperature of the gas is increased by one-fifth and the pressure is increased one and a half times. Calculate the final volume of the gas.
A certain mass of a gas occupies 2 litres at 27°C and 100 Pa. Find the temperature when volume and pressure become half of their initial values.
22.4 litres of gas weighs 70 g at STP. Calculate the weight of the gas if it occupies a volume of 20 litres at 27°C and 700 mmHg of pressure.
State Boyle's Law.
Name or state the following:
The law which studies the relationship between pressure of a gas and the volume occupied by it at constant temperature.
Assuming temperature remaining constant calculate the pressure of the gas in the following:
The pressure of a gas having volume 380 lits. originally occupying 800 cm3 at 76 cm. pressure.
Assuming temperature remaining constant calculate the pressure of the gas in the following:
The pressure of a gas having volume 1800 ml. originally occupying 300 ml. at 6 atms. pressure.
