Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
![Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 7 - Study of Gas Laws Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 7 - Study of Gas Laws - Shaalaa.com](/images/concise-chemistry-english-class-9-icse_6:3baa192b34e3498fa97ae56602d705f0.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 7: Study of Gas Laws
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 7 of CISCE Selina for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE.
Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE 7 Study of Gas Laws Exercise 7 (A) [Pages 125 - 126]
What do you understand by gas?
Give the assumptions of the kinetic molecular theory.
During the practical session in the lab when hydrogen sulphide gas having offensive odour is prepared for some test, we can smell the gas even 50 metres away. Explain the phenomenon.
What is diffusion? Give an example to illustrate it.
How is molecular motion related with temperature?
State (i) the three variables for gas laws and (ii) SI units of these variables.
State Boyle's Law.
Give its
(i) mathematical expression
(ii) graphical representation and
(iii) significance.
Explain Boyle's Law on the basis of the kinetic theory of matter.
The molecular theory states that the pressure exerted by a gas in a closed vessel results from the gas molecules striking against the walls of the vessel. How will the pressure change if
- The temperature is doubled keeping the volume constant
- The volume is made half of its original value keeping the T constant
State Charles's law.
Give its
(i) graphical representation,
(ii) mathematical expression
(iii) significance
Explain Charles's law on the basis of the kinetic theory of matter.
Define absolute zero and absolute scale of temperature. Write about the relationship between °C and K.
What is the need for the Kelvin scale of temperature?
What is the boiling point of water on the Kelvin scale? Convert it into a centigrade scale.
Define S.T.P.
Why is it necessary to compare gases at S.T.P?
Write the value of:
the standard temperature in:
(i) °C
(ii) K
Write the values of:
standard pressure in:
(i) atm
(ii) mm Hg
(iii) cm Hg
(iv) torr
What is the relationship between the Celsius and Kelvin scales of temperature?
Convert (i) 273°C to Kelvin and (ii) 293 K to °C.
State the law which is represented by the following graph:
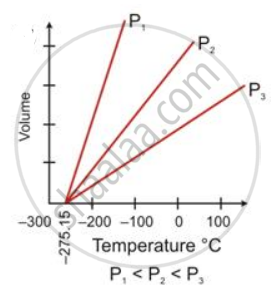
State the law which is represented by the following graph:
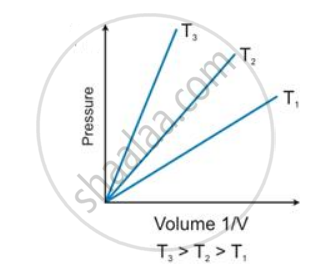
Give reason for the following:
All temperatures in the absolute (Kelvin) scale is in positive figures.
Give reason for the following:
Gases have a lower density compared to solids or liquids.
Give reason for the following:
Gases exert pressure in all directions.
Give reasons for the following:
It is necessary to specify the pressure and temperature of gas while stating its volume.
Give reasons for the following:
Inflating a balloon seems to violate Boyle's law.
Give reasons for the following:
Mountaineers carry oxygen cylinders with them.
Give reasons for the following:
Gas fills the vessel completely in which it is kept.
How did Charles's law lead to the concept of an absolute scale of temperature?
What is meant by aqueous tension? How is the pressure exerted by a gas corrected to account for aqueous tension?
State the following:
The volume of a gas at 0 Kelvin
State the following:
The absolute temperature of a gas at 7°C
State the following:
Gas equation
State the following:
Ice point in absolute temperature
State the following:
STP conditions
Choose the correct answer:
The graph of PV vs P for gas is
Parabolic
Hyperbolic
A straight line parallel to the X-axis
A straight line passing through the origin
Choose the correct answer:
The absolute temperature value that corresponds to 27°C is
200 K
300 K
400 K
246 K
Choose the correct answer:
The volume-temperature relationship is given by
Boyle
Gay-Lussac
Dalton
Charles
Choose the correct answer:
If the pressure is doubled for a fixed mass of a gas, its volume will become
4 times
½ times
2 times
No change
Match the following:
|
|
Column A |
Column B |
|
(a) |
cm3 |
(i) Pressure |
|
(b) |
Kelvin |
(ii) Temperature |
|
(c) |
Torr |
(iii) Volume |
|
(d) |
Boyle's law |
(iv) `"V"/"T" = ("V"_1)/("T"_1)` |
|
(a) |
Charles's law |
(v) `"PV"/"T" = ("P"_1 "V"_1)/"T"_1` |
|
|
|
(vi) PV = P1V1 |
Correct the following statement:
The volume of a gas is inversely proportional to its pressure at a constant temperature.
Correct the following statement:
The volume of a fixed mass of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature, pressure remaining constant.
Correct the following statement:
0°C is equal to zero Kelvin.
Correct the following statement:
The standard temperature is 25°C.
Correct the following statement:
The boiling point of water is 273 K.
Fill in the blanks:
The average kinetic energy of the molecules of a gas is proportional to the ………….
Fill in the blanks:
The temperature on the Kelvin scale at which molecular motion completely ceases is called……………
Fill in the blanks:
If the temperature is reduced to half, ………….. would also reduce to half.
Fill in the blanks:
The melting point of ice is …………. Kelvin.
Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE 7 Study of Gas Laws Exercise 7 (B) [Pages 126 - 127]
What will be the minimum pressure required to compress 500 dm3 of air at 1 bar to 200 dm3 temperature remaining constant?
2 liters of gas is enclosed in a vessel at a pressure of 760 mmHg. If the temperature remains constant, calculate pressure when volume changes to 4 dm3.
At constant temperature, the effect of change of pressure on the volume of a gas was as given below:
|
Pressure in atmosphere |
Volume in liters |
|
0.20 |
112 |
|
0.25 |
89.2 |
|
0.40 |
56.25 |
|
0.60 |
37.40 |
|
0.80 |
28.10 |
|
1.00 |
22.4 |
(a) Plot the following graphs
- P vs V
- P vs 1/V
- PV vs P
Interpret each graph in terms of the law.
(b) Assuming that the pressure values given above are correct, find the correct measurement of the volume.
800 cm3 of gas is collected at 650 mm pressure. At what pressure would the volume of the gas reduce by 40% of its original volume, the temperature remaining constant?
A cylinder of 20 liters capacity contains gas at 100 atmospheric pressure. How many flasks of 200 cm3capacity can be filled from it at 1-atmosphere pressure, temperature remaining constant?
A steel cylinder of internal volume 20 litres is filled with hydrogen at 29 atmospheric pressure. If hydrogen is used to fill a balloon at 1.25 atmospheric pressure at the same temperature, what volume will the gas occupy?
561 dm3 of a gas at STP is filled in a 748 dm3 container. If the temperature is constant, calculate the percentage change in pressure required.
88 cm3 of nitrogen is at a pressure of 770 mm mercury. If the pressure is raised to 880 mmHg, find by how much the volume will diminish, the temperature remaining constant.
A gas at 240 K is heated to 127°C. Find the percentage change in the volume of the gas (pressure remaining constant).
A certain amount of a gas occupies a volume of 0.4 litre at 17°C. To what temperature should it be heated so that its volume gets (a) doubled, (b) reduced to half, pressure remaining constant?
A given mass of a gas occupied 143 cm3 at 27° C and 700 mm Hg pressure. What will be its volume at 300 K and 280 mm Hg pressure?
A gas occupies 500 cm3 at a normal temperature. At what temperature will the volume of the gas be reduced by 20% of its original volume, the pressure is constant?
Calculate the final volume of a gas 'X' if the original pressure of the gas at STP is doubled and its temperature is increased three times.
A sample of carbon dioxide occupies 30 cm3 at 15°C and 740 mm pressure. Find its volume at STP.
What temperature would be necessary to double the volume of a gas initially at s.t.p. if the pressure is decreased by 50%?
At 0°C and 760 mmHg pressure, a gas occupies a volume of 100 cm3. Kelvin temperature of the gas is increased by one-fifth and the pressure is increased one and a half times. Calculate the final volume of the gas.
It is found that on heating a gas its volume increases by 50% and its pressure decreases to 60% of its original value. If the original temperature was -15°C, find the temperature to which it was heated.
A certain mass of a gas occupies 2 litres at 27°C and 100 Pa. Find the temperature when volume and pressure become half of their initial values.
2500 cm3 of hydrogen is taken at STP. The pressure of this gas is further increased by two and a half times (temperature remaining constant). What volume will hydrogen occupy now?
Taking the volume of hydrogen as calculated in Q.19, what change must be made in Kelvin (absolute) temperature to return the volume to 2500 cm3 (pressure remaining constant)?
A given amount of gas A is confined in a chamber of constant volume. When the chamber is immersed in a bath of melting ice, the pressure of the gas is 100 cmHg.
- What is the temperature when the pressure is 10cmHg?
- What will be the pressure when the chamber is brought to 100°C
A gas is to be filled from a tank of capacity 10,000 litres into cylinders each having capacity of 10 litres. The condition of the gas in the tank is as follows:
- The pressure inside the tank is 800 mm of Hg.
- The temperature inside the tank is −3°C.
When the cylinder is filled, the pressure gauge reads 400 mm of Hg and the temperature is 270 K. Find the number of cylinders required to fill the gas.
Calculate the volume occupied by 2 g of hydrogen at 27°C and 4-atmosphere pressure if at STP it occupies 22.4 litres.
50 cm3 of hydrogen is collected over water at 17°C and 750 mmHg pressure. Calculate the volume of a dry gas at STP. The water vapour pressure at 17°C is 14 mmHg.
Which will have greater volume when the following gases are compared at STP:
- 1.2/N2 at 25°C and 748 mmHg
- 1.25/O2 at STP
Calculate the volume of dry air at STP that occupies 28 cm3 at 14°C and 750 mmHg pressure when saturated with water vapour. The vapour pressure of water at 14°C is 12 mmHg.
An LPG cylinder can withstand a pressure of 14.9 atmospheres. The pressure gauge of the cylinder indicates 12 atmospheres at 27°C. Because of a sudden fire in the building, the temperature rises. At what temperature will the cylinder explode?
22.4 litres of gas weighs 70 g at STP. Calculate the weight of the gas if it occupies a volume of 20 litres at 27°C and 700 mmHg of pressure.
Solutions for 7: Study of Gas Laws
![Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 7 - Study of Gas Laws Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 7 - Study of Gas Laws - Shaalaa.com](/images/concise-chemistry-english-class-9-icse_6:3baa192b34e3498fa97ae56602d705f0.jpg)
Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 7 - Study of Gas Laws
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Selina solutions for Mathematics Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE CISCE 7 (Study of Gas Laws) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Selina textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 7 Study of Gas Laws are Molecular Motion : Relationship of Temperature, Pressure and Volume, The Temperature and a Thermometer, The Gas Laws, Scales of Thermometers, Gas Equation, Standard Temperature Pressure (S.T.P.), The Effect of Moisture and Pressure, Gases and Its Characteristics, Pressure and Volume Relationship or Bolye's Law, Temperature - Volume Relationship or Charles's Law, Absolute Zero.
Using Selina Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE solutions Study of Gas Laws exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Selina Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE students prefer Selina Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 7, Study of Gas Laws Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE additional questions for Mathematics Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
