Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Give reason for the following:
Gases exert pressure in all directions.
Gases unlike solids and liquids exert pressure in all directions.
उत्तर १
The gas particles have a very weak attractive force between them and move randomly ultimately exert pressure in all direction. Their molecules are bouncing all around the container because they are so small, then gravity has very little effect on them.
उत्तर २
Impact of gas molecules with high velocity causes pressure to be exerted on the walls.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain Why?
"When stating the volume of a gas, the pressure and temperature should also be given."
What is meant by aqueous tension? How is the pressure exerted by a gas corrected to account for aqueous tension?
State the following:
The absolute temperature of a gas at 7°C
Convert the following pressure value into Pascals.
107000 Nm−2
Convert 101.325 kPa to bar.
Identify the gas laws from the following diagram.
| Diagram | Gas laws |
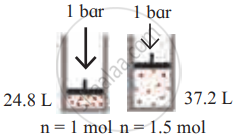 |
______________ |
Solve the following.
A balloon is inflated with helium gas at room temperature of 25°C and at 1 bar pressure when its initial volume is 2.27L and allowed to rise in the air. As it rises in the air external pressure decreases and the volume of the gas increases till finally, it bursts when external pressure is 0.3bar. What is the limit at which the volume of the balloon can stay inflated?
Solve the following.
The volume of a given mass of a gas at 0°C is 2 dm3. Calculate the new volume of the gas at constant pressure when the temperature is increased by 10°C.
Use of hot air balloon in sports and meteorological observation is an application of
Hydrochloric acid is treated with a metal to produce hydrogen gas. Suppose a student carries out this reaction and collects a volume of 154.4 × 10−3 dm3 of a gas at a pressure of 742 mm of Hg at a temperature of 298 K. What mass of hydrogen gas (in mg) did the student collect?
