Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Solve the following.
The volume of a given mass of a gas at 0°C is 2 dm3. Calculate the new volume of the gas at constant pressure when the temperature is increased by 10°C.
उत्तर
Given:
T1 = Initial temperature = 0°C = 0 + 273.15 = 273.15 K,
V1 = Initial volume = 2 dm3
T2 = Final temperature = 273.15 K + 10 = 283.15 K
To find: V2 = Final volume
Formula: `"V"_1/"T"_1="V"_2/"T"_2` (at constant n and P)
Calculation:
According to Charles’ law,
`"V"_1/"T"_1="V"_2/"T"_2` (at constant n and P)
∴ V2 = `("V"_1"T"_2)/"T"_1=(2xx283.15)/273.15` = 2.073 dm3
The new volume of a given mass of gas is 2.073 dm3
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain Why?
"When stating the volume of a gas, the pressure and temperature should also be given."
What would be the mass of CO2 occupying a volume of 44 litres at 25°C and 750 mm pressure.
Give reason for the following:
Gases have a lower density compared to solids or liquids.
State the following:
The absolute temperature of a gas at 7°C
Convert the following temperature from degree Celcius to kelvin.
−15° C
Convert the following pressure value into Pascals.
1 kPa
Convert 101.325 kPa to bar.
Convert −100° C to kelvin
Convert 0.124 torr to the standard atmosphere
Identify the gas laws from the following diagram.
| Diagram | Gas laws |
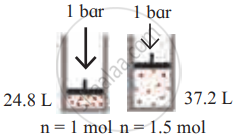 |
______________ |
Consider a sample of a gas in a cylinder with a movable piston.
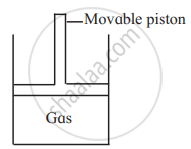
Show diagrammatically the changes in the position of the piston, if the temperature is decreased from 300 K to 150 K at constant pressure.
Consider a sample of a gas in a cylinder with a movable piston.

Show diagrammatically the changes in the position of the piston, if the temperature is decreased from 400 K to 300 K, and pressure is decreased from 4 bar to 3 bar.
Match the pairs of the following:
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| a. Boyle’s law | i. at constant pressure and volume |
| b. Charles’ law | ii. at constant temperature |
| iii. at constant pressure |
Write the statement for Charles’ law
Solve the following.
A hot air balloon has a volume of 2800 m3 at 99°C. What is the volume if the air cools to 80°C?

Solve the following.
At 0°C, a gas occupies 22.4 liters. How much hot must be the gas in celsius and in kelvin to reach a volume of 25.0 liters?
Explain the following observation.
Aerated water bottles are kept under water during summer
Explain the following observation.
Liquid ammonia bottle is cooled before opening the seal
Explain the following observation.
The type of an automobile is inflated to slightly lesser pressure in summer than in winter
A sample of gas has a volume of 8.5 dm3 at an unknown temperature. When the sample is submerged in ice water at 0°C, its volume gets reduced to 6.37 dm3. What is its initial temperature?
Of two samples of nitrogen gas, sample A contains 1.5 moles of nitrogen in a vessel of the volume of 37.6 dm3 at 298 K, and sample B is in a vessel of volume 16.5 dm3 at 298 K. Calculate the number of moles in sample B.
At what temperature, the volume of gas would become zero?
The number of molecules in 8.96 litres of gas at 0°C and 1 atm. pressure is approximately ______.
