Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Solve the following.
A hot air balloon has a volume of 2800 m3 at 99°C. What is the volume if the air cools to 80°C?

उत्तर
Given:
V1 = Initial volume = 2800 m3,
T1 = Initial temperature = 99°C = 99 + 273.15 = 372.15 K,
T2 = Final temperature = 80°C = 80 + 273.15 K = 353.15 K
To find: V2 = Final volume
Formula: `"V"_1/"T"_1="V"_2/"T"_2` (at constant n and P)
Calculation:
According to Charles’ law,
`"V"_1/"T"_1="V"_2/"T"_2` (at constant n and P)
∴ V2 = `("V"_1"T"_2)/"T"_1=(2800xx353.15)/372.15` = 2657 m3
The volume of the balloon when the air cools to 80°C is 2657 m3
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain Why?
"When stating the volume of a gas, the pressure and temperature should also be given."
State (i) the three variables for gas laws and (ii) SI units of these variables.
Give reason for the following:
Gases have a lower density compared to solids or liquids.
Answer in one sentence.
A bubble of methane gas rises from the bottom of the North sea. What will happen to the size of the bubble as it rises to the surface?
Convert the following pressure value into Pascals.
107000 Nm−2
Convert exactly 1.5 atm to pascals
Convert −100° C to kelvin
Hot air balloons float in the air because of the low density of the air inside the balloon. Explain this with the help of an appropriate gas law.

Identify the gas laws from the following diagram.
| Diagram | Gas laws |
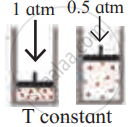 |
______________ |
Consider a sample of a gas in a cylinder with a movable piston.
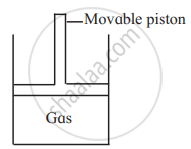
Show diagrammatically the changes in the position of the piston, if the temperature is decreased from 300 K to 150 K at constant pressure.
With the help of the graph answer the following -

At constant temperature, the Graph shows the relationship between pressure and volume. Represent the relation mathematically.
With the help of the graph answer the following -

At constant temperature, Write the statement of law.
Solve the following.
A balloon is inflated with helium gas at room temperature of 25°C and at 1 bar pressure when its initial volume is 2.27L and allowed to rise in the air. As it rises in the air external pressure decreases and the volume of the gas increases till finally, it bursts when external pressure is 0.3bar. What is the limit at which the volume of the balloon can stay inflated?
State Boyle's law.
Name two items that can serve as a model for Gay Lusaac’s law and explain.
Give the mathematical expression that relates gas volume and moles.
Explain the following observation.
The size of a weather balloon becomes larger and larger as it ascends up to larger altitude
Of two samples of nitrogen gas, sample A contains 1.5 moles of nitrogen in a vessel of the volume of 37.6 dm3 at 298 K, and sample B is in a vessel of volume 16.5 dm3 at 298 K. Calculate the number of moles in sample B.
Sulphur hexafluoride is a colourless, odourless gas; calculate the pressure exerted by 1.82 moles of the gas in a steel vessel of volume 5.43 dm3 at 69.5 °C, assuming ideal gas behaviour
At 25°C and 1 atm, a cylinder containing 10 L of an ideal gas is connected to the empty cylinder with a capacity of 20 L. The pressures exerted by gas m both the cylinders will be ____________.
For a given mass of an ideal gas, which of the following statements is CORRECT?
According to Andrews isothermals at what temperature the carbon dioxide gas starts to condense at 73 atmosphere?
If 2 moles of an ideal gas at 546 K has volume of 44.8 L, then what will be it's pressure? (R = 0.082)
10 g of gas at one atomospheric pressure is cooled from 273.15°C to 0°C keeping the volume constant. What is the final pressure?
At what temperature, the volume of gas would become zero?
