Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain Charles's law on the basis of the kinetic theory of matter.
उत्तर
Charles's law on the basis of the kinetic theory of matter:
According to the kinetic theory of matter, the average kinetic energy of gas molecules is directly proportional to the absolute temperature. Thus, when the temperature of a gas is increased, the molecules would move faster and the molecules will strike the unit area of the walls of the container more frequently and vigorously. If the pressure is kept constant, the volume increases proportionately. Hence, at constant pressure, the volume of a given mass of a gas is directly proportional to the temperature (Charles's law).
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State the law which is represented by the following graph:
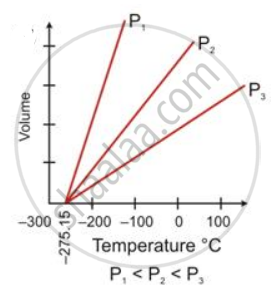
State the following:
Ice point in absolute temperature
Calculate the final volume of a gas 'X' if the original pressure of the gas at STP is doubled and its temperature is increased three times.
An LPG cylinder can withstand a pressure of 14.9 atmospheres. The pressure gauge of the cylinder indicates 12 atmospheres at 27°C. Because of a sudden fire in the building, the temperature rises. At what temperature will the cylinder explode?
State Charles's law.
Correct the following statement:
The volume of a fixed mass of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature, pressure remaining constant.
A certain mass of gas occupied 850 ml at a pressure of 760 mm of Hg. On increasing the pressure it was found that the volume of the gas was 75% of its initial value. Assuming constant temperature, find the final pressure of the gas?
Fill in the blank with the correct word, from the words in option:
At -273°C the volume of a gas is theoretically ______.
A fixed volume of a gas occupies 760cm3 at 27°C and 70 cm of Hg. What will be its vol. at s.t.p.
The following question refers to one mole of chlorine gas.
What volume will it occupy at 273°C?
