Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A battery of e.m.f. 6·0 V supplies current through a circuit in which the resistance can be changed. A high resistance voltmeter is connected across the battery. When the current is 3 A, the voltmeter reads 5.4 V. Find the internal resistance of the battery.
उत्तर
Since a battery's terminal potential difference is less than its e.m.f., an increase in circuit current causes the voltmeter reading to fall.
Now E = 6.0 V,
V = 5.4 V,
I = 3.0 A
Internal resistance r = `("E" - "V")/"I"`
= `(6 - 5.4)/3.0`
= `0.3/1.5`
r = 0.2 Ω
संबंधित प्रश्न
A cell of e.m.f ε and internal resistance r is used to send current to an external resistance R. Write expressions for
- the total resistance of circuit.
- the current drawn from the cell.
- the p.d. across the cell.
- voltage drop inside the cell.
A cell is used to send current to an external circuit.
- How does the voltage across its terminals compare with its e.m.f.?
- Under what condition is the e.m.f. of a cell equal to its terminal voltage?
The diagram below in Fig. 8.40 shows a cell of e.m.f. ε = 2 volt and internal resistance r = 1 ohm to an external resistance R = 4 ohm. The ammeter A measures the current in the circuit and the
voltmeter V measures the terminal voltage across the cell. What will be the readings of the ammeter and voltmeter when (i) the key K is open, (ii) the key K is closed.

A battery of e.m.f 3.0 V supplies current through a circuit in which the resistance can be changed.
A high resistance voltmeter is connected across the battery. When the current is 1.5 A, the voltmeter reads 2.7 V. Find the internal resistance of the battery.
A cell of e.m.f. 1.8V and internal resistance 2Ω is connected in series with an ammeter of resistance 0.7Ω and a resistor of 4.5Ω as shown in Fig.
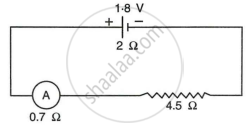
- What would be the reading of the ammeter?
- What is the potential difference across the terminals of the cell?
A battery of e.m.f. 15 V and internal resistance 3 ohm is connected to two resistors of resistances 3 ohm and 6 ohm is series Find:
(a) the current through the battery
(b) the p.d. between the terminals of the battery.
A cell of e.m.f. 2 V and internal resistance 1.2 Ω is connected to an ammeter of resistance 0.8 Ω and two resistors of 4.5 Ω and 9 Ω as shown in following figure.

Find:
- The reading of the ammeter,
- The potential difference across the terminals of the cells, and
- The potential difference across the 4.5 Ω resistor.
Four cells, each of e.m.f. 1.5 V and internal resistance 2.0 ohms are connected in parallel. The battery of cells is connected to an external resistance of 2.5 ohms. Calculate:
(i) The total resistance of the circuit.
(ii) The current flowing in the external circuit.
(iii) The drop in potential across-the terminals of the cells.
Define the e.m.f. (E) of a cell and the potential difference (V) of a resistor R in terms of the work done in moving a unit charge. State the relation between these two works and the work done in moving a unit charge through a cell connected across the resistor. Take the internal resistance of the cell as ‘r’. Hence obtain an expression for the current i in the circuit.
Study the diagram:
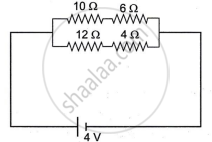
- Calculate the total resistance of the circuit.
- Calculate the current drawn from the cell.
- State whether the current through 10 Ω resistor is greater than, less than or equal to the current through the 12 Ω resistor.
