Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A body is falling freely under the action of gravity alone in vacuum. Which of the following quantities remain constant during the fall?
विकल्प
Kinetic energy.
Potential energy.
Total mechanical energy.
Total linear momentum.
उत्तर
Total mechanical energy.
Explanation:
As the body is falling freely under gravity, the potential energy decreases continuously and kinetic energy increases continuously as all the conservative forces are doing work. So, the total mechanical energy (PE + KE) of the body will be constant.
Let us discuss this in detail:
In the given diagram an object is dropped from-a height H from the ground.
At a point, The total mechanical energy will be EA = K.E + P.E
`E_A = 1/2 mv^2 + mgH`
As velocity will be zero at A, so its kinetic energy will be zero.
`E_A = mgH`
Velocity at point B will be, `v_B = sqrt(2gh)`
So energy at point B will be `E_B = KE + PE`
`E_B = 1/2 m(2gh) + mg(H - h)`
`E_B = mgh + mgH - mgh`
`E_B = mgH`
Now, velocity at point C will be `v_c = sqrt(2gh)`
So, energy at point C will be `E_C = KE + PE`
So, total mechanical energy will remain the same (if we neglect the air friction).
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A heavy stone is thrown from a cliff of height h with a speed v. The stoen will hit the ground with maximum speed if it is thrown
A heavy stone is thrown in from a cliff of height h in a given direction. The speed with which it hits the ground
(a) must depend on the speed of projection
(b) must be larger than the speed of projection
(c) must be independent of the speed of projection
(d) may be smaller than the speed of projection.
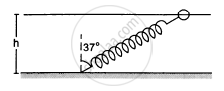
One end of a spring of natural length h and spring constant k is fixed at the ground and the other is fitted with a smooth ring of mass m which is allowed to slide on a horizontal rod fixed at a height h (following figure). Initially, the spring makes an angle of 37° with the vertical when the system is released from rest. Find the speed of the ring when the spring becomes vertical.
A spring of negligible mass and force constant 5 Nm–1 is compressed by a distance x = 5 cm. A block of mass 200 g is free to leave the end of the spring. If the system is released, what will be the speed of the block when it leaves the spring?
A particle is released from height S from the surface of the Earth. At a certain height, its kinetic energy is three times its potential energy. The height from the surface of the earth and the speed of the particle at that instant are respectively ______.
Two inclined frictionless tracks, one gradual and the other steep meet at A from where two stones are allowed to slide down from rest, one on each track as shown in figure.
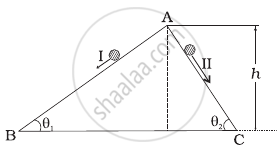
Which of the following statement is correct?
A mass of 5 kg is moving along a circular path of radius 1 m. If the mass moves with 300 revolutions per minute, its kinetic energy would be ______.
In a shotput event an athlete throws the shotput of mass 10 kg with an initial speed of 1 ms–1 at 45° from a height 1.5 m above ground. Assuming air resistance to be negligible and acceleration due to gravity to be 10 ms–2, the kinetic energy of the shotput when it just reaches the ground will be ______.
A body falls towards earth in air. Will its total mechanical energy be conserved during the fall? Justify.
A baloon filled with helium rises against gravity increasing its potential energy. The speed of the baloon also increases as it rises. How do you reconcile this with the law of conservation of mechanical energy? You can neglect viscous drag of air and assume that density of air is constant.
