Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A mass of 5 kg is moving along a circular path of radius 1 m. If the mass moves with 300 revolutions per minute, its kinetic energy would be ______.
विकल्प
250 π2
100 π2
5 π2
0
उत्तर
A mass of 5 kg is moving along a circular path of radius 1 m. If the mass moves with 300 revolutions per minute, its kinetic energy would be `underline(250 π^2)`.
Explanation:
Given, mass = m = 5 kg
Radius = 1 m = R
Revolution per minute ω = 300 rev/min
= (300 × 2π) rad/min
= (300 × 2 × 3.14) rad/60 s
= `(300 xx 2 xx 3.14)/60` rad/s
= 10 × rad/s
⇒ Linear speed = v = ωR
= `((300 xx 2π)/60) (1m)`
= 10π m/s
KE = `1/2 mv^2`
= `1/2 xx 5 xx (10π)^2`
= `100π^2 xx 5 xx 1/2`
= 250 π2 J
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A particle is rotated in a vertical circle by connecting it to a string of length l and keeping the other end of the string fixed. The minimum speed of the particle when the string is horizontal for which the particle will complete the circle is
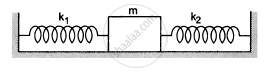
A block of mass m is attached to two unstretched springs of spring constants k1 and k2 as shown in the following figure. The block is displaced towards the right through a distance x and is released. Find the speed of the block as it passes through the mean position shown.
A small heavy block is attached to the lower end of a light rod of length l which can be rotated about its clamped upper end. What minimum horizontal velocity should the block be given so that it moves in a complete vertical circle?
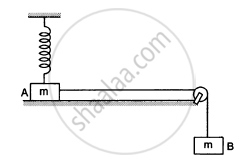
In the following figure shows two blocks A and B, each of mass of 320 g connected by a light string passing over a smooth light pulley. The horizontal surface on which the block Acan slide is smooth. Block A is attached to a spring of spring constant 40 N/m whose other end is fixed to a support 40 cm above the horizontal surface. Initially, the spring is vertical and unstretched when the system is released to move. Find the velocity of the block A at the instant it breaks off the surface below it. Take g = 10 m/s2.
One end of a spring of natural length h and spring constant k is fixed at the ground and the other is fitted with a smooth ring of mass m which is allowed to slide on a horizontal rod fixed at a height h (following figure). Initially, the spring makes an angle of 37° with the vertical when the system is released from rest. Find the speed of the ring when the spring becomes vertical.
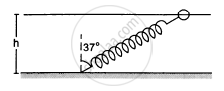
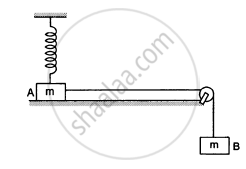
Figure following shows a light rod of length l rigidly attached to a small heavy block at one end and a hook at the other end. The system is released from rest with the rod in a horizontal position. There is a fixed smooth ring at a depth h below the initial position of the hook and the hook gets into the ring as it reaches there. What should be the minimum value of h so that the block moves in a complete circle about the ring?
A body is falling freely under the action of gravity alone in vacuum. Which of the following quantities remain constant during the fall?
Two inclined frictionless tracks, one gradual and the other steep meet at A from where two stones are allowed to slide down from rest, one on each track as shown in figure.
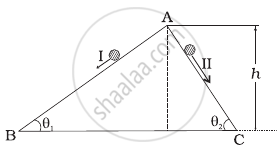
Which of the following statement is correct?
Which of the diagrams shown in figure represents variation of total mechanical energy of a pendulum oscillating in air as function of time?
A body falls towards earth in air. Will its total mechanical energy be conserved during the fall? Justify.
