Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A bolt of mass 0.3 kg falls from the ceiling of an elevator moving down with an uniform speed of 7 m s–1. It hits the floor of the elevator (length of the elevator = 3 m) and does not rebound. What is the heat produced by the impact? Would your answer be different if the elevator were stationary?
उत्तर १
Mass of the bolt, m = 0.3 kg
Speed of the elevator = 7 m/s
Height, h = 3 m
Since the relative velocity of the bolt with respect to the lift is zero, at the time of impact, potential energy gets converted into heat energy.
Heat produced = Loss of potential energy
= mgh = 0.3 × 9.8 × 3
= 8.82 J
The heat produced will remain the same even if the lift is stationary. This is because of the fact that the relative velocity of the bolt with respect to the lift will remain zero.
उत्तर २
P.E. of bolt = mgh = 0.3 x 9.8 x 3 = 8.82 J
The bolt does not rebound. So the whole of the energy is converted into heat. Since the value of acceleration due to gravity is the same in all inertial system, therefore the answer will not change even if the elevator is stationary
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The casing of a rocket in flight burns up due to friction. At whose expense is the heat energy required for burning obtained? The rocket or the atmosphere?
Comets move around the sun in highly elliptical orbits. The gravitational force on the comet due to the sun is not normal to the comet’s velocity in general. Yet the work done by the gravitational force over every complete orbit of the comet is zero. Why?
A rain drop of radius 2 mm falls from a height of 500 m above the ground. It falls with decreasing acceleration (due to viscous resistance of the air) until at half its original height, it attains its maximum (terminal) speed, and moves with uniform speed thereafter. What is the work done by the gravitational force on the drop in the first and second half of its journey? What is the work done by the resistive force in the entire journey if its speed on reaching the ground is 10 m s–1?
A projectile is fired from the top of a 40 m high cliff with an initial speed of 50 m/s at an unknown angle. Find its speed when it hits the ground.
On complete combustion a litre of petrol gives off heat equivalent to 3 × 107 J. In a test drive a car weighing 1200 kg. including the mass of driver, runs 15 km per litre while moving with a uniform speed on a straight track. Assuming that friction offered by the road surface and air to be uniform, calculate the force of friction acting on the car during the test drive, if the efficiency of the car engine were 0.5.
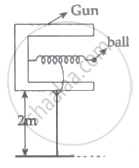
In a spring gun having spring constant 100 N/m a small ball 'B' of mass 100 g is put in its barrel (as shown in figure) by compressing the spring through 0.05 m. There should be a box placed at a distance 'd' on the ground so that the ball falls in it. If the ball leaves the gun horizontally at a height of 2 m above the ground. The value of d is ______ m.
(g = 10 m/s2).
A wedge of mass M = 4m lies on a frictionless plane. A particle of mass m approaches the wedge with speed v. There is no friction between the particle and the plane or between the particle and the wedge. The maximum height climbed by the particle on the wedge is given by ______.
