Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A car accelerates to a velocity of 30 m/s in 10 s and then decelerates for 20 s so that it stops. Draw a velocity-time graph to represent the motion and find:
Distance travelled
उत्तर
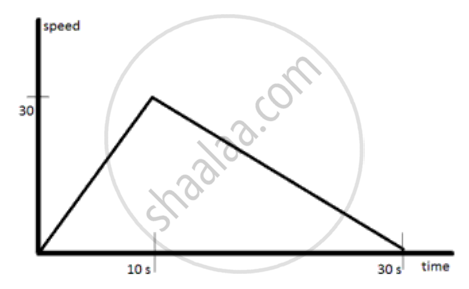
Distance travelled= area under speed time graph = `1/2`x30x30 =450 m.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A body is moving vertically upwards. Its velocity changes at a constant rate from 50 m s-1 to 20 m s-1 in 3 s. What is its acceleration?
A body falls freely from a certain height. Show graphically the relation between the distance fallen and square of time. How will you determine g from this graph?
A space craft flying in a straight course with velocity of 75 km s-1 fires its rocket motors for 6.0 s. At the end of this time its speed is 120 km s-1 in the same direction.
Find
(i) The space craft's average acceleration while the motors were firing
(ii) The distance travelled by the space craft in the first 10 s after the rocket motors were started, the motors being in action for only 6 s.
Give an example of an accelerated body, moving with a uniform speed.
The change in velocity of a motorbike is 54 kmh−1 in one minute. Calculate its acceleration in (a) ms−2 (b) kmh−2.
From the velocity – time graph given below, calculate deceleration in region BC.

Convert the following acceleration:
7200 km/h2 into m/s2
Assertion: The accelerated motion of an object may be due to change in magnitude of velocity or direction or both of them.
Reason: Acceleration can be produced only by change in magnitude of the velocity. It does not depend the direction.
Exercise Problem.
A racing car has a uniform acceleration of 4 ms–2. What distance it covers in 10 s after the start?
Acceleration is a scalar.
