Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Assertion: The accelerated motion of an object may be due to change in magnitude of velocity or direction or both of them.
Reason: Acceleration can be produced only by change in magnitude of the velocity. It does not depend the direction.
विकल्प
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
If assertion is true but reason is false.
If assertion is false but reason is true.
उत्तर
If assertion is true but reason is false.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
An object of mass 16 kg is moving with an acceleration of 3 m/s2. Calculate the applied force. If the same force is applied to an object of mass 24 kg, how much will be the acceleration?
Define acceleration. State its unit.
The velocity-time graph for a uniformly retarded body is a straight line inclined to the time axis with an obtuse angle. How is retardation calculated from the velocity-time graph?
Diagram is given below shows velocity – time graph of car P and Q, starting from the same place and in the same direction. Calculate the Acceleration of car P.

The acceleration of a moving body is constant in magnitude and direction. Must the path of the body be a straight line?
If not, given an example.
Interpret the following graph: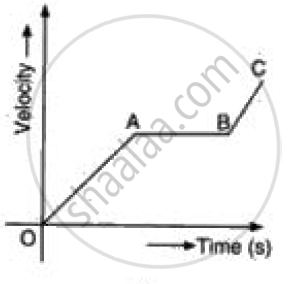
What happens to the stepwise increasing speed-time graph when the size of each step is made very small?
A car accelerates to a velocity of 30 m/s in 10 s and then decelerates for 20 s so that it stops. Draw a velocity-time graph to represent the motion and find:
The Deceleration.
Figure represents graphically the velocity of a car moving along a straight road over a period of 100 hours.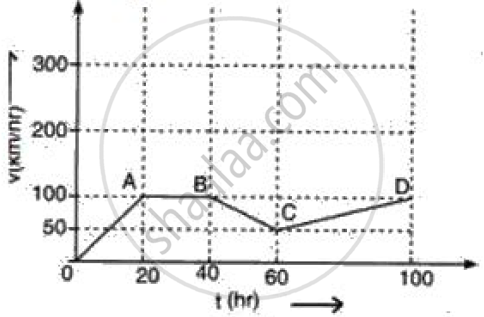
Calculate the acceleration along AB and the retardation along BC.
If a body starts from rest, what can be said about the acceleration of the body?
