Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
An object of mass 16 kg is moving with an acceleration of 3 m/s2. Calculate the applied force. If the same force is applied to an object of mass 24 kg, how much will be the acceleration?
उत्तर
Given: m1 = 16 kg, a1 = 3 m/s2, m2 = 24 kg
Find: a2 = ?, F = ?
Applied force, F = m1a1 = 16 kg × 3 m/s2 = 48 N
∴ F = m2a2
∴ Acceleration, `"a"_2 = "F"/"m"_2`
`= (48 "N")/(24 "kg")`
= 2 m/s2
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Give a scientific reason.
When an object falls freely to the ground, its acceleration is uniform.
The unit of retardation is ____________
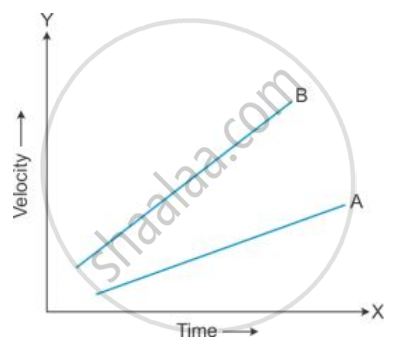
Figure shows the velocity-time graphs for two cars A and B moving in the same direction. Which car has greater acceleration? Give reasons to your answer.
A body falls freely from a certain height. Show graphically the relation between the distance fallen and square of time. How will you determine g from this graph?
A space craft flying in a straight course with velocity of 75 km s-1 fires its rocket motors for 6.0 s. At the end of this time its speed is 120 km s-1 in the same direction.
Find
(i) The space craft's average acceleration while the motors were firing
(ii) The distance travelled by the space craft in the first 10 s after the rocket motors were started, the motors being in action for only 6 s.
From the diagram given below, calculate acceleration.

Diagram is given below shows velocity – time graph of car P and Q, starting from the same place and in the same direction. Calculate the Acceleration of car P.

A racing car, initially at rest, picks up a velocity of 180 kmh−1 in 4.5 s. Calculate
- acceleration
- distance covered by the car.
A motor bike running at 5 ms−1, picks up a velocity of 30 ms−1 in 5s. Calculate
- acceleration
- distance covered during acceleration.
The acceleration of a moving body is constant in magnitude and direction. Must the path of the body be a straight line?
If not, given an example.
Write the SI unit of retardation.
What happens to the stepwise increasing speed-time graph when the size of each step is made very small?
A body has an acceleration of -3.5 ms-2. What is its retardation?
Convert the following acceleration:
7200 km/h2 into m/s2
Convert the following acceleration:
1/36 m/s2 into km/h2
The graph shows how the velocity of a scooter varies with time in 50 s.
Work out: Acceleration.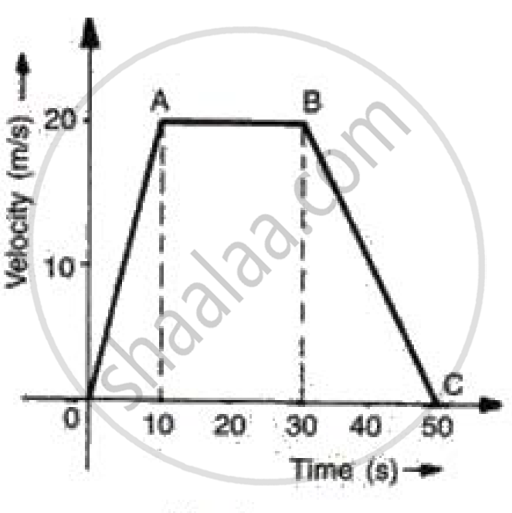
Figure represents graphically the velocity of a car moving along a straight road over a period of 100 hours.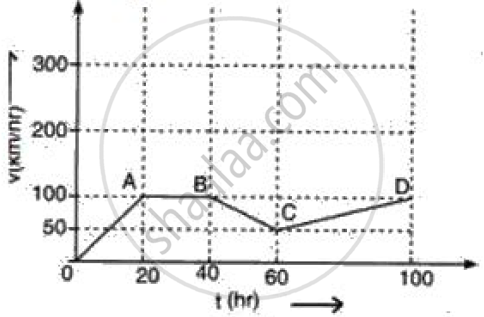
Calculate the acceleration along AB and the retardation along BC.
Negative acceleration is called ______.
It is possible to have objects moving with uniform speed but variable acceleration.
Assertion: A positive acceleration of a body can be associated with the slowing down of the body.
Reason: Acceleration is a vector.
