Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
An object of mass 16 kg is moving with an acceleration of 3 m/s2. Calculate the applied force. If the same force is applied to an object of mass 24 kg, how much will be the acceleration?
Solution
Given: m1 = 16 kg, a1 = 3 m/s2, m2 = 24 kg
Find: a2 = ?, F = ?
Applied force, F = m1a1 = 16 kg × 3 m/s2 = 48 N
∴ F = m2a2
∴ Acceleration, `"a"_2 = "F"/"m"_2`
`= (48 "N")/(24 "kg")`
= 2 m/s2
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The unit of retardation is ____________
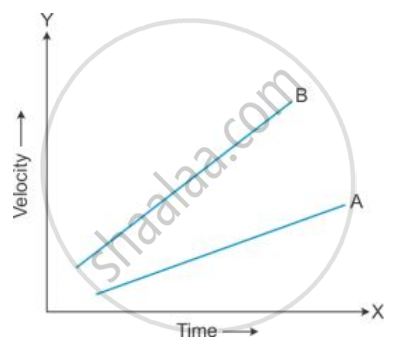
Figure shows the velocity-time graphs for two cars A and B moving in the same direction. Which car has greater acceleration? Give reasons to your answer.
A body falls freely from a certain height. Show graphically the relation between the distance fallen and square of time. How will you determine g from this graph?
If a body is moving with a constant velocity its acceleration is ______.
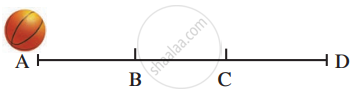
A ball is rolling from A to D on a flat and smooth surface. Its speed is 2 cm/s. On reaching B, it was pushed continuously up to C. On reaching D from C, its speed had become 4 cm/s. It took 2 seconds for it to go from B to C. What is the acceleration of the ball as it goes from B to C?
Draw velocity – time graph for the following situation:
When a body is moving with variable velocity and variable acceleration.
A motorbike, initially at rest, picks up a velocity of 72 kmh−1 over a distance of 40 m. Calculate
- acceleration
- time in which it picks up above velocity.
A racing car, initially at rest, picks up a velocity of 180 kmh−1 in 4.5 s. Calculate
- acceleration
- distance covered by the car.
A body falls towards the earth. Does it have positive or negative acceleration?
The speed of a car increases from 10 km/h to 64 km/h in 10 seconds. What will be its acceleration?
State if the following situation is possible:
A body moving with a constant velocity in an accelerated motion.
A car accelerates uniformly from a velocity of 18 km/h to 36 km/h in 15 min. What is its acceleration?
A car accelerates to a velocity of 30 m/s in 10 s and then decelerates for 20 s so that it stops. Draw a velocity-time graph to represent the motion and find:
The Deceleration.
Figure represents graphically the velocity of a car moving along a straight road over a period of 100 hours.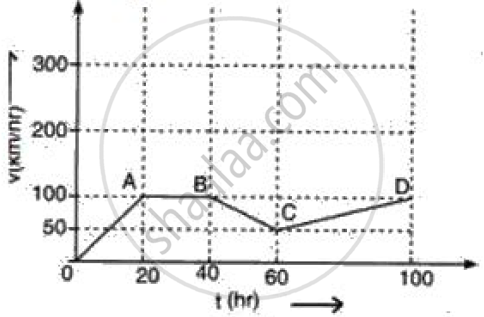
Calculate the acceleration along AB and the retardation along BC.
The slope of a velocity-time graph gives ______.
When a body starts from rest, the acceleration of the body after 2 seconds in ______ of its displacement.
The acceleration of the body that moves with a uniform velocity will be ______.
When an object undergoes acceleration ______.
The value of acceleration for a body at rest is ______.
Assertion: When a body is subjected to a uniform acceleration, it is always moving in a straight line.
Reason: Motion may be straight-line motion or circular motion.
