Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
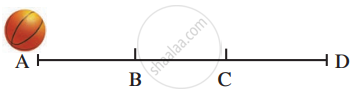
A ball is rolling from A to D on a flat and smooth surface. Its speed is 2 cm/s. On reaching B, it was pushed continuously up to C. On reaching D from C, its speed had become 4 cm/s. It took 2 seconds for it to go from B to C. What is the acceleration of the ball as it goes from B to C?
Solution
The acceleration of the ball between A to B is zero as the speed and direction of the ball are constant. After point B, a force is applied. Thus, the ball will get accelerated.
`"Acceleration of the ball from B to C" = "Change in velocity from B to C"/"Time taken for this change"`
`"Acceleration of the ball from B to C" = (4 - 2)/2 = 1m"/"s^2`
RELATED QUESTIONS
The change in velocity of a motorbike is 54 kmh−1 in one minute. Calculate its acceleration in (a) ms−2 (b) kmh−2.
State if the following situation is possible:
A body moving with a constant velocity in an accelerated motion.
A car accelerates uniformly from a velocity of 18 km/h to 36 km/h in 15 min. What is its acceleration?
The graph shows how the velocity of a scooter varies with time in 50 s.
Work out: Deceleration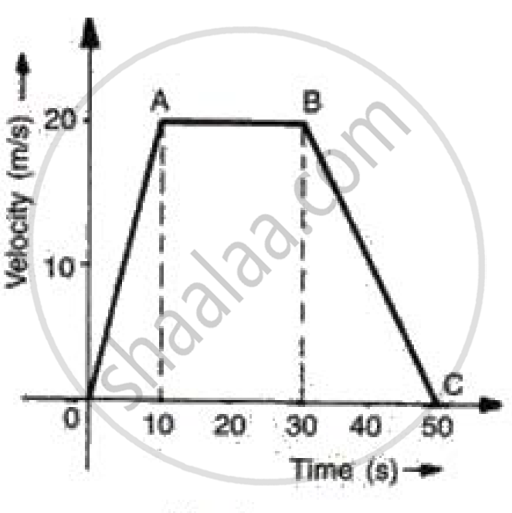
The rate of change of velocity is ______.
State whether true or false. If false, correct the statement.
Acceleration can get negative value also.
When a body starts from rest, the acceleration of the body after 2 seconds in ______ of its displacement.
The speed of a particle is constant. Will it have acceleration? Justify with an example.
A car is being driven at a speed of 20ms-1 when brakes are applied to bring it to rest in 5 s. The deceleration produced in this case will be ______.
Assertion: A negative acceleration of a body can be associated with speeding up of the body.
Reason: Increase in the speed of a moving body is independent of its direction of motion.
