Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
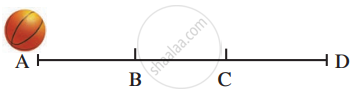
A ball is rolling from A to D on a flat and smooth surface. Its speed is 2 cm/s. On reaching B, it was pushed continuously up to C. On reaching D from C, its speed had become 4 cm/s. It took 2 seconds for it to go from B to C. What is the acceleration of the ball as it goes from B to C?
उत्तर
The acceleration of the ball between A to B is zero as the speed and direction of the ball are constant. After point B, a force is applied. Thus, the ball will get accelerated.
`"Acceleration of the ball from B to C" = "Change in velocity from B to C"/"Time taken for this change"`
`"Acceleration of the ball from B to C" = (4 - 2)/2 = 1m"/"s^2`
संबंधित प्रश्न
Distinguish between acceleration and retardation.
Figure given below shows a velocity-time graph for a car starting from rest. The graph has three parts AB, BC and CD.
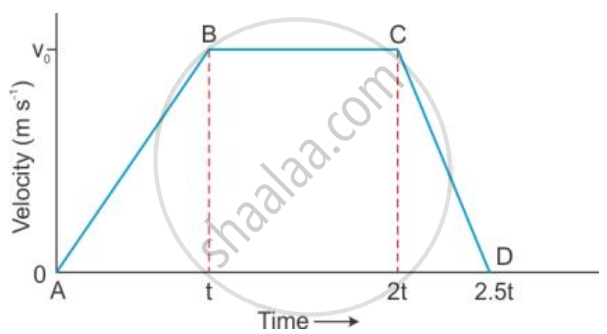
(a) Is the magnitude of acceleration higher or lower than that of retardation ? Give a reason .
(b) Compare the magnitude of acceleration and retardation .
The change in velocity of a motorbike is 54 kmh−1 in one minute. Calculate its acceleration in (a) ms−2 (b) kmh−2.
An aeroplane lands at 216 kmh−1 and stops after covering a runway of 2 m. Calculate the acceleration and the time, in which it comes to rest.
A truck running at 90 kmh−1, is brought to rest over a distance of 25 m. Calculate the retardation and time for which brakes are applied.
What is the SI unit of acceleration?
Interpret the following graph: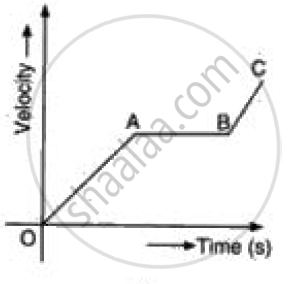
A car starts from rest and it is travelling with a velocity of 20 m/s in 10 s. What is its acceleration?
If a moving body comes to rest, then its acceleration is ______.
An object can be moving with uniform speed but with variable acceleration.
