Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
An aeroplane lands at 216 kmh−1 and stops after covering a runway of 2 m. Calculate the acceleration and the time, in which it comes to rest.
उत्तर
Initial velocity = u = 216 kmh−1
u = `216xx5/18` = 60 ms−1
Final velocity = v = 0
Distance = S = 2 km = 2000 m
v2 − u2 = 2aS
(0)2 − (60)2 = 2a (2000)
4000 a = −3600
(Acceleration) a = `(-3600)/4000`
= −0.9 ms−2
Now, v = u + at
0 = 60 + (−0.9)t
0.9t = 60
(Time) t = `60/0.9=600/9` = 66.67 S
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State the type of motion represented by the following sketches in Figures.
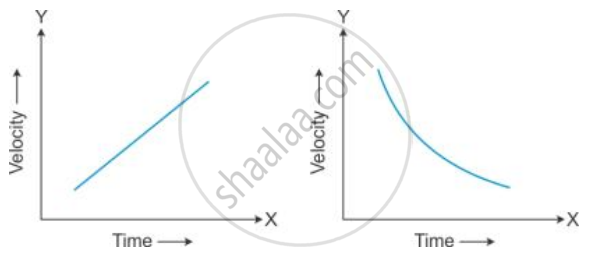
Give an example of each type of motion.
A train starts from rest and accelerates uniformly at a rate of 2 m s-2 for 10 s. It then maintains a constant speed for 200 s. The brakes are then applied and the train is uniformly retarded and comes to rest in 50 s. Find
(i) The maximum velocity reached,
(ii) The retardation in the last 50 s,
(iii) The total distance travelled,
(iv) The average velocity of the train.
When is the acceleration due to gravity negative?
The change in velocity of a motorbike is 54 kmh−1 in one minute. Calculate its acceleration in (a) ms−2 (b) kmh−2.
A cyclist driving at 5 ms−1, picks a velocity of 10 ms−1, over a distance of 50 m. Calculate
- acceleration
- time in which the cyclist picks up above velocity.
Write the SI unit of acceleration and retardation.
The distance covered by a body is directly proportional to the square of the time elapsed. What can you say about its acceleration?
A car accelerates to a velocity of 30 m/s in 10 s and then decelerates for 20 s so that it stops. Draw a velocity-time graph to represent the motion and find:
Distance travelled
A car starts from rest and it is travelling with a velocity of 20 m/s in 10 s. What is its acceleration?
A car is being driven at a speed of 20ms-1 when brakes are applied to bring it to rest in 5 s. The deceleration produced in this case will be ______.
