Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A body falls freely from a certain height. Show graphically the relation between the distance fallen and square of time. How will you determine g from this graph?
Solution
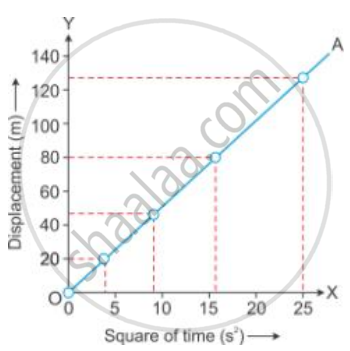
The value of acceleration due to gravity (g) can be obtained by doubling the slope of the S - t2 graph for a freely falling body.
RELATED QUESTIONS
The velocity-time graph for a uniformly retarded body is a straight line inclined to the time axis with an obtuse angle. How is retardation calculated from the velocity-time graph?
A car travels with uniform velocity of 25 m s-1 for 5 s. The brakes are then applied and the car is uniformly retarded and comes to rest in further 10 s. Find:
- The distance which the car travels before the brakes are applied,
- Retardation and
- The distance travelled by car after applying the brakes.
A vehicle is accelerating on a straight road. Its velocity at any instant is 30 km/h. After 2 s, it is 33.6 km/h, and after further 2 s, it is 37.2 km/h. Find the acceleration of the vehicle in m s-2. Is the acceleration uniform?
A truck running at 90 kmh−1, is brought to rest over a distance of 25 m. Calculate the retardation and time for which brakes are applied.
Define acceleration.
Distinguish between uniformly and non-uniformly accelerated motions.
What happens to the stepwise increasing speed-time graph when the size of each step is made very small?
What do you understand about negative acceleration?
Assertion: A positive acceleration of a body can be associated with the slowing down of the body.
Reason: Acceleration is a vector.
When a body is said to be in
- uniform acceleration
- non–uniform acceleration?
