Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Figure represents graphically the velocity of a car moving along a straight road over a period of 100 hours.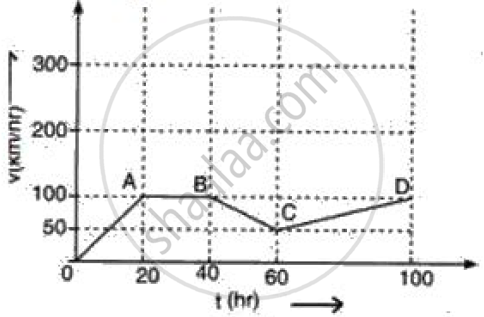
Calculate the acceleration along AB and the retardation along BC.
उत्तर

Acceleration along AB= (100 - 100)/(40 -20) = 0 ms-2
Retardation along CD= (100 - 50)/ (100 - 60) = 50/40 = 1.25 ms-2
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State the type of motion represented by the following sketches in Figures.
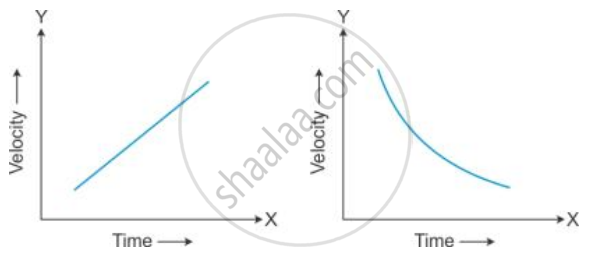
Give an example of each type of motion.
The velocity-time graph for a uniformly retarded body is a straight line inclined to the time axis with an obtuse angle. How is retardation calculated from the velocity-time graph?
A body falls freely from a certain height. Show graphically the relation between the distance fallen and square of time. How will you determine g from this graph?
A vehicle is accelerating on a straight road. Its velocity at any instant is 30 km/h. After 2 s, it is 33.6 km/h, and after further 2 s, it is 37.2 km/h. Find the acceleration of the vehicle in m s-2. Is the acceleration uniform?
From the diagram given below, calculate acceleration.

From the velocity – time graph given below, calculate deceleration in region BC.

A car traveling at 60 km/h, stops on applying brakes in 10 seconds. What is its acceleration?
State if the following situation is possible:
A body moving with constant acceleration but with Zero velocity.
What happens to the stepwise increasing speed-time graph when the size of each step is made very small?
Correct your friend who says that acceleration gives the idea of how fast the position changes.
