Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
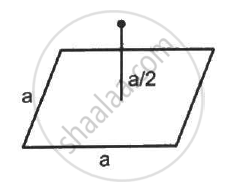
A charge Q is placed at a distance a/2 above the centre of a horizontal, square surface of edge a as shown in the following figure . Find the flux of the electric field through the square surface.
उत्तर
Given:-
Edge length of the square surface = a
Distance of the charge Q from the square surface = a/2
Area of the plane = a2
Assume that the given surface is one of the faces of the imaginary cube.
Then, the charge is found to be at the centre of the cube.
A charge is placed at a distance of about `"a"/2` from the centre of the surface.
The electric field due to this charge is passing through the six surfaces of the cube.
Hence flux through each surface,
`phi = "Q"/∈_0 xx 1/6 = "Q"/(6∈_0)`
Thus, the flux through the given surface is `"Q"/(6∈_0).`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Mark out the correct options.
Two large conducting plates are placed parallel to each other with a separation of 2⋅00 cm between them. An electron starting from rest near one of the plates reaches the other plate in 2⋅00 microseconds. Find the surface charge density on the inner surfaces.
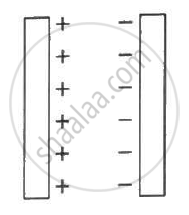
Two large conducting plates are placed parallel to each other and they carry equal and opposite charges with surface density σ as shown in the figure. Find the electric field (a) at the left of the plates (b) in between the plates and (c) at the right of the plates.
Two particles A and B, each with a charge Q, are placed a distance d apart. Where should a particle of charge q be placed on the perpendicular bisector of AB, so that it experiences maximum force? What is the magnitude of this maximum force?
A positive charge Q is distributed uniformly over a circular ring of radius R. A particle of mass m, and a negative charge q, is placed on its axis at a distance x from the centre. Find the force on the particle. Assuming x << R, find the time period of oscillation of the particle if it is released from there .
A conducting sphere of radius 0.104 m has an unknown charge. If the electric field at 0.20 m from the centre of the sphere is 1.5 x 103 NC-1 and points radially inward, what is the electric flux?
Conductors are materials that allow ______.
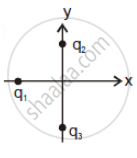
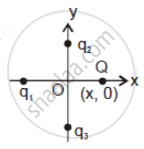
In figure two positive charges q2 and q3 fixed along the y-axis, exert a net electric force in the + x-direction on a charge q1 fixed along the x-axis. If a positive charge Q is added at (x, 0), the force on q1 ______.
(1) |
(2) |
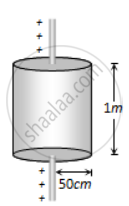
Electric charge is uniformly distributed along a long straight wire of radius 1 mm. The charge per cm length of the wire is Q coulomb. Another cylindrical surface of radius 50 cm and length 1 m symmetrically enclose the wire as shown in the figure. The total electric flux passing through the cylindrical surface is ______.
When a glass rod is rubbed with silk, it ______.
Which of the following graphs shows the variation of electric field E due to a hollow spherical conductor of radius R as a function of distance from the centre of the sphere?
Which one of the following is the unit of electric charge?
A positive charge particle of 100 mg is thrown in opposite direction to a uniform electric field of strength 1 × 105 NC–1. If the charge on the particle is 40 μC and the initial velocity is 200 ms-1, how much distance it will travel before coming to the rest momentarily ______.
Given below are two statements:
- Statement I: The electric force changes the speed of the charged particle and hence changes its kinetic energy; whereas the magnetic force does not change the kinetic energy of the charged particle.
- Statement II: The electric force accelerates the positively charged particle perpendicular to the direction of the electric field. The magnetic force accelerates the moving charged particle along the direction of the magnetic field.
In light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below.
Two identical conducting spheres with negligible volume have 2.1 nC and -0.1 nC charges, respectively. They are brought into contact and then separated by a distance of 0.5 m. The electrostatic force acting between the spheres is ______ × 10-9N.
[Given: 4πε0 = `1/(9xx10^9)` SI unit]
The potential at a point x (measured in µm) due to some charges situated on the X-axis is given by v(x) = `20/((x^2 - 4)` V. The electric field E at x = 4 µm is given by ______.
