Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A charge Q is placed at a distance a/2 above the centre of a horizontal, square surface of edge a as shown in the following figure . Find the flux of the electric field through the square surface.
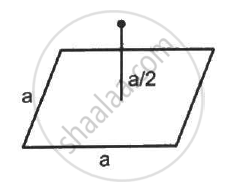
Solution
Given:-
Edge length of the square surface = a
Distance of the charge Q from the square surface = a/2
Area of the plane = a2
Assume that the given surface is one of the faces of the imaginary cube.
Then, the charge is found to be at the centre of the cube.
A charge is placed at a distance of about `"a"/2` from the centre of the surface.
The electric field due to this charge is passing through the six surfaces of the cube.
Hence flux through each surface,
`phi = "Q"/∈_0 xx 1/6 = "Q"/(6∈_0)`
Thus, the flux through the given surface is `"Q"/(6∈_0).`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Write the expression for the displacement current in terms of the rate of change of electric flux.
A point charge is brought inside an electric field. The electric field at a nearby point
(a) will increase if the charge is positive
(b) will decrease if the charge is negative
(c) may increase if the charge is positive
(d) may decrease if the charge is negative
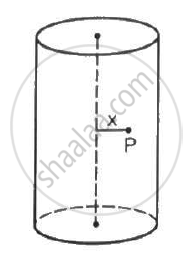
A long cylindrical volume contains a uniformly distributed charge of density ρ. Find the electric field at a point P inside the cylindrical volume at a distance x from its axis (see the figure).
A rod of length L has a total charge Q distributed uniformly along its length. It is bent in the shape of a semicircle. Find the magnitude of the electric field at the centre of curvature of the semicircle.
A smple pendulum consists of a small sphere of mass m suspended by a thread of length l. The sphere carries a positive charge q. The pendulum is placed in a uniform electric field of strength E directed vertically downwards. Find the period of oscillation of the pendulum due to the electrostatic force acting on the sphere, neglecting the effect of the gravitational force.
A positively charged glass rod is brought close to a metallic rod isolated from ground. The charge on the side of the metallic rod away from the glass rod will be ______.
Choose the correct option.
Two point charges of +5 μC are so placed that they experience a force of 8.0 × 10-3N. They are then moved apart so that the force is now 2.0 × 10-3N. The distance between them is now
Answer the following question.
What is the magnitude of the charge on an electron?
Two parallel plates have a potential difference of 10 V between them. If the plates are 0.5 mm apart, what will be the strength of electric charge.
When 1019 electrons are removed from a neutral metal plate through some process, the electric charge on it is ______
Two small conducting spheres of equal radius have charges +10 µC and -20 µC respectively and placed at a distance R from each other experience force F1· If they are brought in contact and separated to the same distance, they experience force F2. The ratio of F1 to F2 is ____________.
A conducting sphere of radius 0.104 m has an unknown charge. If the electric field at 0.20 m from the centre of the sphere is 1.5 x 103 NC-1 and points radially inward, what is the electric flux?
Equal charge are given to two-sphere of different radii. The potential will be
A positive charge particle of 100 mg is thrown in opposite direction to a uniform electric field of strength 1 × 105 NC–1. If the charge on the particle is 40 μC and the initial velocity is 200 ms-1, how much distance it will travel before coming to the rest momentarily ______.
Given below are two statements:
- Statement I: The electric force changes the speed of the charged particle and hence changes its kinetic energy; whereas the magnetic force does not change the kinetic energy of the charged particle.
- Statement II: The electric force accelerates the positively charged particle perpendicular to the direction of the electric field. The magnetic force accelerates the moving charged particle along the direction of the magnetic field.
In light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below.
A straight infinitely long cylinder of radius R0 = 10 cm is uniformly charged with a surface charge density σ = + 10-12 C/m2. The cylinder serves as a source of electrons, with the velocity of the emitted electrons perpendicular to its surface. Electron velocity must be ______ × 105 m/s to ensure that electrons can move away, from the axis of the cylinder to a distance greater than r = 103 m.
A charge of magnitude 3e and mass 2m is moving in an electric field E. The acceleration imparted to the charge is ______.
