Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer the following question.
A charged particle q is moving in the presence of a magnetic field B which is inclined to an angle 30° with the direction of the motion of the particle. Draw the trajectory followed by the particle in the presence of the field and explain how the particle describes this path.
उत्तर
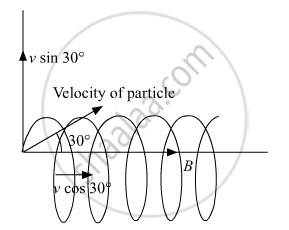
Lorentz force will be exerted on the particle because of the Sine component of particle velocity thereby making the particle move in a helical path.
Time period = `("Total distance")/("speed") = (2"πR")/("v"_"y") (2"πR")/("v" sin 30°) = (4"πR")/("v")`
Pitch = speed along x-axis × time period
`= "v"_x xx (2"πR")/("v"_"y")`
`= "v"_x xx (2"πR")/("v"sin30°) = "v"_x xx (2"πR" xx 2)/("v")`
= `"v" cos 30° xx (4"πR")/("v") = sqrt(3)/(2) xx 4"πR" = 2sqrt(3)"πR"`
R = `(mv sin 30°)/(q"B")`
Pitch = `(2sqrt(3)"πmv" sin 30°)/(q"B")`
= `(2sqrt(3)"πmv")/(q"B" xx2)`
= `(sqrt(3)"πmv")/(q"B")`
The vertical component of velocity will make the charged particle to move in a circular path whereas the horizontal component of velocity will provide Pitch = `(sqrt(3)"πmv")/(q"B")` Hence the motion of the particle will be helical with the Pitch= `(sqrt(3)"πmv")/(q"B")`.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Answer the following question, which help you understand the difference between Thomson’s model and Rutherford’s model better.
Is the average angle of deflection of α-particles by a thin gold foil predicted by Thomson’s model much less, about the same, or much greater than that predicted by Rutherford’s model?
In a Geiger-Marsden experiment, calculate the distance of closest approach to the nucleus of Z = 80, when a α-particle of 8Mev energy impinges on it before it comes momentarily to rest and reverses its direction.
How will the distance of closest approach be affected when the kinetic energy of the α-particle is doubles?
The first line of Balmer series (Hα) in the spectrum of hydrogen is obtained when an electron of hydrogen atom goes from ______.
If the radius of second electron orbit in hydrogen atom be r then the radius of the third orbit will be ______.
An automobile moves on a road with a speed of 54 km h−1. The radius of its wheels is 0.45 m and the moment of inertia of the wheel about its axis of rotation is 3 kg m2. If the vehicle is brought to rest in l 5s, the magnitude of average torque transmitted by its brakes to the wheel is:
Plutonium decays with half of 24000 years. If plutonium is store for 72000 yrs. The fraction of .its that remain:-
The radius of electron's second stationary orbit in Bohr's atom is R. The radius of 3rd orbit will be:-
The ratio active Nude 7N13 decays 6C13 through the emission of
The ratio of minimum to maxm wavelength in ballmer series is:-
According to Bohr model, magnetic field at centre (at the nucleus) of a hydrogen atom due to motion of electron in the ninth orbit is proportional to:
