Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Answer the following question.
A charged particle q is moving in the presence of a magnetic field B which is inclined to an angle 30° with the direction of the motion of the particle. Draw the trajectory followed by the particle in the presence of the field and explain how the particle describes this path.
Solution
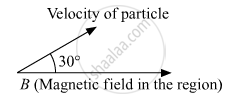
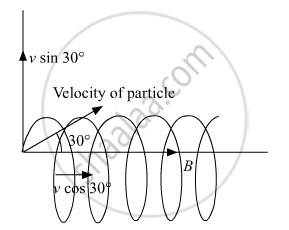
Lorentz force will be exerted on the particle because of the Sine component of particle velocity thereby making the particle move in a helical path.
Time period = `("Total distance")/("speed") = (2"πR")/("v"_"y") (2"πR")/("v" sin 30°) = (4"πR")/("v")`
Pitch = speed along x-axis × time period
`= "v"_x xx (2"πR")/("v"_"y")`
`= "v"_x xx (2"πR")/("v"sin30°) = "v"_x xx (2"πR" xx 2)/("v")`
= `"v" cos 30° xx (4"πR")/("v") = sqrt(3)/(2) xx 4"πR" = 2sqrt(3)"πR"`
R = `(mv sin 30°)/(q"B")`
Pitch = `(2sqrt(3)"πmv" sin 30°)/(q"B")`
= `(2sqrt(3)"πmv")/(q"B" xx2)`
= `(sqrt(3)"πmv")/(q"B")`
The vertical component of velocity will make the charged particle to move in a circular path whereas the horizontal component of velocity will provide Pitch = `(sqrt(3)"πmv")/(q"B")` Hence the motion of the particle will be helical with the Pitch= `(sqrt(3)"πmv")/(q"B")`.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Using Rutherford's model of the atom, derive the expression for the total energy of the electron in hydrogen atom. What is the significance of total negative energy possessed by the electron?
Answer the following question, which help you understand the difference between Thomson’s model and Rutherford’s model better.
Is the probability of backward scattering (i.e., scattering of α-particles at angles greater than 90°) predicted by Thomson’s model much less, about the same, or much greater than that predicted by Rutherford’s model?
Answer the following question, which help you understand the difference between Thomson’s model and Rutherford’s model better.
In which model is it completely wrong to ignore multiple scattering for the calculation of average angle of scattering of α-particles by a thin foil?
The total energy of an electron in the ground state of the hydrogen atom is -13·6 eV. Its total energy, when a hydrogen atom is in the first excited state, is ______.
For 7.7 Mev alpha particles scattering from aluminium (Z = 13), the distance of closest approach in a bead on collision is ______.
Useful data
`1/(4 pi ∈_0) = 8.99 xx 10^9` newton m2C-2; c = 1.60 × 10-19 C; leV = 1.60 × 10-19j.
Which one of the following statements does not hold good when two balls of masses m1 and m2 undergo elastic collision?
The Bohr model for the H-atom relies on the Coulomb’s law of electrostatics. Coulomb’s law has not directly been verified for very short distances of the order of angstroms. Supposing Coulomb’s law between two opposite charge + q1, –q2 is modified to |F| = `(q_1q_2)/((4πε_0)) 1/r^2, r ≥ R_0 = (q_1q_2)/(4πε_0) 1/R_0^2 (R_0/r)^ε, r ≤ R_0` Calculate in such a case, the ground state energy of a H-atom, if ε = 0.1, R0 = 1Å.
The energy of hydrogen atom in an orbit is −1.51 eV. What are the kinetic and potential energies of the electron in this orbit?
The shortest wavelength of the Brackett series of a hydrogen like atom of atomic number Z is same as the shortest wavelength of the Balmer series of hydrogen atom, then the value of Z is ______.
Differentiate between the 'distance of the closest approach' and the 'impact parameter.'
