Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A father's age is three times the sum of the ages of his two children. After 5 years his age will be two times the sum of their ages. Find the present age of the father.
उत्तर
Let the sum of ages of two sons be x years
Age of man = 3x years
After 5 years age of the man = (3x + 5)years
Sum of ages of two sons =( x+10) years
Given, (3x+5)=2( x+10)
⇒ (3x+5) = 2x+ 20
⇒ x = 15
Hence 3x - 3(15) =45
Thus the age of the man(father) is 45 years.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A card is drawn at random from a well-shuffled deck of playing cards. Find the probability that the card drawn is a black king.
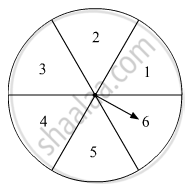
In fig. 7 is shown a disc on which a player spins an arrow twice. The fraction `a/b` is formed, where 'a' is the number of sector on which arrow stops on the first spin and 'b' is the number of the sector in which the arrow stops on second spin. On each spin, each sector has equal chance of selection by the arrow. Find the probability that the fraction `a/b>1.`
Two different coins are tossed simultaneously. The probability of getting at least one head is
(A)`1/2`
(B)`1/8`
(C)`3/4`
(D)`7/8`
Choose the correct alternative answer for the following question.
There are 40 cards in a bag. Each bears a number from 1 to 40. One card is drawn at random. What is the probability that the card bears a number which is a multiple of 5 ?
A box contains 20 cards numbered from 1 to 20. A card is drawn at random from the box. Find the probability that the number on the drawn card is divisible by 2 or 3
Red queens and black jacks are removed from a pack of 52 playing cards. A card is drawn at random from the remaining cards, after reshuffling them. Find the probability that the card drawn is a king
A die is thrown once. What is the probability of getting a number greater than 4?
Which of the following cannot be the probability of an event?
The probability that a number selected at random from the numbers 1, 2, 3, ..., 15 is a multiple of 4, is
Two different coins are tossed simultaneously. The probability of getting at least one head is
All red face cards are removed from a pack of playing cards. The remaining cards are well shuffled and then a card is drawn at random from them. Find the probability that the drawn card is a face card.
By using two variables, write the following statement in mathematical form:
The cost of two tables and five chairs is 2,200.
Find If A If tan 2A = cot (A-24°)
A die is thrown once. Find the probability of getting a composite number
A coin is tossed. What is the probability of getting:
a tail?
A die is thrown once. Find the probability of getting:
a number less than 6
A lot consists of 144 ball pens of which 20 are defective and the others are good. Tanu will buy a pen if it is good but will not buy it if it is defective. The shopkeeper draws one pen at random and gives it to her. The probability that she will buy that pen is ____________.
I toss three coins together. The possible outcomes are no heads, 1 head, 2 heads and 3 heads. So, I say that probability of no heads is `1/4`. What is wrong with this conclusion?
Getting a prime number on throwing a die is an event.
A card is drawn at random from a pack of well shuffled 52 playing cards. Complete the following activity to find the probability that the card drawn is:
Event A: The card drawn is an ace.
Event B: The card drawn is a spade.
Activity: 'S' is the sample space.
∴ n(S) = 52
Event A: The card drawn is an ace.
∴ n(A) = `square`
P(A) = `square` ......(formula)
∴ P(A) = `square/52`
∴ P(A) = `square/13`
Event B: The card drawn is a spade.
∴ n(B) = `square`
P(B) = `(n(B))/(n(S))`
∴ P(B) = `square/4`
