Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A paisa coin is made up of Al-Mg alloy and weighs 0.75g. It has a square shape and its diagonal measures 17 mm. It is electrically neutral and contains equal amounts of positive and negative charges.
Treating the paisa coins made up of only Al, find the magnitude of equal number of positive and negative charges. What conclusion do you draw from this magnitude?
उत्तर
1 Molar mass M of Al has NA = 6.023 × 1023 atoms.
∴ m = mass of Al paisa coin has N = NA m/M atoms
Now, ZAl = 13, MAl = 26.9815 g
Hence N = 6.02 × 1023 atoms/mol × 0.75/26.9815g/mol
= 1.6733 × 1022 atoms
∴ q = +ve charge in paisa = N Ze
= (1.67 × 1022)(13) (1.60 × 10–19C)
= 3.48 × 104 C
q = 34.8 kC of ±ve charge.
This is an enormous amount of charge. Thus we see that ordinary neutral matter contains an enormous amount of ± charges.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why can one ignore quantisation of electric charge when dealing with macroscopic i.e., large scale charges?
When a glass rod is rubbed with a silk cloth, charges appear on both. A similar phenomenon is observed with many other pairs of bodies. Explain how this observation is consistent with the law of conservation of charge.
It is now believed that protons and neutrons (which constitute nuclei of ordinary matter) are themselves built out of more elementary units called quarks. A proton and a neutron consist of three quarks each. Two types of quarks, the so called ‘up’ quark (denoted by u) of charge (+2/3) e, and the ‘down’ quark (denoted by d) of charge (−1/3) e, together with electrons build up ordinary matter. (Quarks of other types have also been found which give rise to different unusual varieties of matter.) Suggest a possible quark composition of a proton and neutron.
Does the charge given to a metallic sphere depend on whether it is hollow or solid? Give reason for your answer.
A point charge is taken from a point A to a point B in an electric field. Does the work done by the electric field depend on the path of the charge?
Answer the following question.
State the law of conservation of charge.
+2 C and +6 C two charges are repelling each other with a force of 12 N. If each charge is given -2 C of charge, then the value of the force will be ______
Charge is quantized means ______.
A glass rod rubbed with silk is used to charge a gold-leaf electroscope and the leaves are observed to diverge. The electroscope thus charged is exposed to X-rays for a short period. Then ______
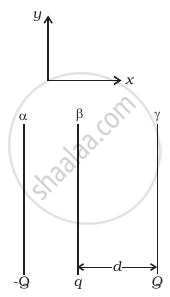
Two fixed, identical conducting plates (α and β), each of surface area S are charged to –Q and q, respectively, where Q > q > 0. A third identical plate (γ), free to move is located on the other side of the plate with charge q at a distance d (Figure). The third plate is released and collides with the plate β. Assume the collision is elastic and the time of collision is sufficient to redistribute charge amongst β and γ.
- Find the electric field acting on the plate γ before collision.
- Find the charges on β and γ after the collision.
- Find the velocity of the plate γ after the collision and at a distance d from the plate β.