Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
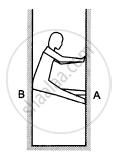
A person (40 kg) is managing to be at rest between two vertical walls by pressing one wall A by his hands and feet and the other wall B by his back (in the following figure). Assume that the friction coefficient between his body and the walls is 0.8 and that limiting friction acts at all the contacts. (a) Show that the person pushes the two wall with equal force. (b) Find the normal force exerted by either wall on the person. Take g = 10 m/s2.
उत्तर
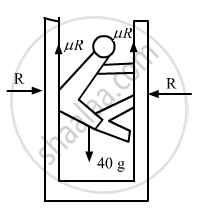
Thus, we have:
μR + μR = mg
⇒ 2μR = 40 × 10
`=>"R" = (40xx10)/(2xx0.8)=250 "N"`
Normal force = 250 N
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A body of mass M is kept on a rough horizontal surface (friction coefficient = μ). A person is trying to pull the body by applying a horizontal force but the body is not moving. The force by the surface on A is F, where
A block A kept on an inclined surface just begins to slide if the inclination is 30°. The block is replaced by another block B and it is found that it just begins to slide if the inclination is 40°.
A boy of mass M is applying a horizontal force to slide a box of mass M' on a rough horizontal surface. The coefficient of friction between the shoes of the boy and the floor is μ and that between the box and the floor is μ'. In which of the following cases it is certainly not possible to slide the box?
Suppose the block of the previous problem is pushed down the incline with a force of 4 N. How far will the block move in the first two seconds after starting from rest? The mass of the block is 4 kg.
A body starts slipping down an incline and moves half metre in half second. How long will it take to move the next half metre?
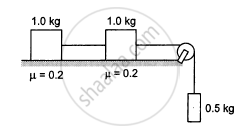
Consider the situation shown in the following figure. Calculate (a) the acceleration of the 1.0 kg blocks, (b) the tension in the string connecting the 1.0 kg blocks and (c) the tension in the string attached to 0.50 kg.
If the tension in the string in the following figure is 16 N and the acceleration of each block is 0.5 m/s2, find the friction coefficients at the two contact with the blocks.
The friction co-efficient between the table and the block shown in the following figure is 0.2. Find the tensions in the two strings.
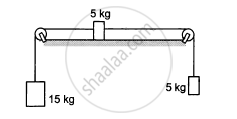
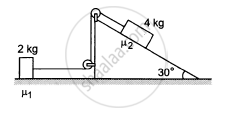
In the following figure shows two blocks in contact sliding down an inclined surface of inclination 30°. The friction coefficient between the block of mass 2.0 kg and the incline is μ1, and that between the block of mass 4.0 kg and incline is μ2. Calculate the acceleration of the 2.0 kg block if (a) μ1 = 0.20 and μ2 = 0.30, (b) μ1 = 0.30 and μ2 = 0.20. Take g = 10 m/s2.
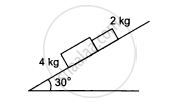
A block of mass M is kept on a rough horizontal surface. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the surface is μ. The block is to be pulled by applying a force to it. What minimum force is needed to slide the block? In which direction should this force act?
The friction coefficient between the board and the floor shown in the following figure is μ. Find the maximum force that the man can exert on the rope so that the board does not slip on the floor.
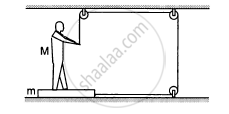
A 2 kg block is placed over a 4 kg block and both are placed on a smooth horizontal surface. The coefficient of friction between the block is 0.20. Find the acceleration of the two blocks if a horizontal force of 12 N is applied to (a) the upper block, (b) the lower block. Take g = 10 m/s2.
The friction coefficient between the two blocks shown in the following figure is μ but the floor is smooth. (a) What maximum horizontal force F can be applied without disturbing the equilibrium of the system? (b) Suppose the horizontal force applied is double of that found in part (a). Find the accelerations of the two masses.
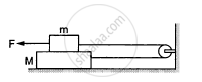
Suppose the entire system of the previous questions is kept inside an elevator which is coming down with an acceleration a < g. Repeat parts (a) and (b).
Consider the situation shown in the following figure. Suppose a small electric field E exists in the space in the vertically charge Q on its top surface. The friction coefficient between the two blocks is μ but the floor is smooth. What maximum horizontal force F can be applied without disturbing the equilibrium?
[Hint: The force on a charge Q bye the electric field E is F = QE in the direction of E.]
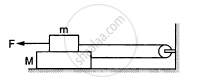
A block of mass m slips on a rough horizontal table under the action of a horizontal force applied to it. The coefficient of friction between the block and the table is μ. The table does not move on the floor. Find the total frictional force applied by the floor on the legs of the table. Do you need the friction coefficient between the table and the floor or the mass of the table?
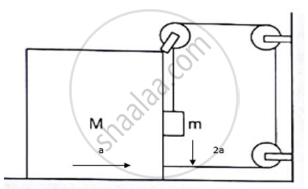
Find the acceleration of the block of mass M in the situation of figure in the following. The coefficient of friction between the two blocks is μ1 and that between the bigger block and the ground is μ2.
A block placed on a rough horizontal surface is pulled by a horizontal force F. Let f be the force applied by the rough surface on the block. Plot a graph of f versus F.
The coefficient of static friction between a wooden block of mass 0.5 kg and a vertical rough wall is 0.2. The magnitude of horizontal force that should be applied on the block to keep it adhered to the wall will be ______ N. [g = 10 ms-2]
An inclined plane is bent in such a way that the vertical cross-section is given by Y = `x^2/4` where y is in vertical and x in horizontal direction. If the upper surface of this curved plane is rough with coefficient of friction µ = 0.5, the maximum height in cm at which a stationary block will not slip downward is ______ cm.
